Introduction
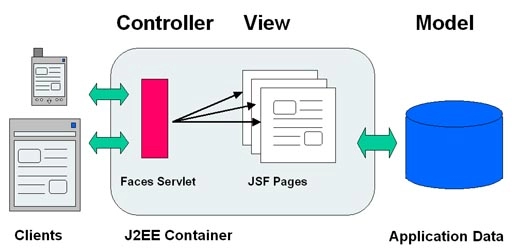
In this blog, we will learn about the JSF h:panelGrid. JSF (Java Server Faces) is a Java-based web application framework designed to build web-based user interfaces more accessible. The Java Community Process codified a definition for JavaServer Faces, a standardised display technology. The MVC design pattern separates model and display, allowing developers to concentrate on their primary competencies and communicate more effectively. The h:selectOneMenu tag creates an HTML input element of type "select" with an unspecified size. A single select HTML input element of type "select" with no specified size is rendered using the JSF h:selectOneMenu tag. This article describes the selectOneMenu function in JSF, beginning with the most straightforward statements and progressing to the most significant modules.
h:selectOneMenu HTML Tag
The Java Community Process codified a definition for JavaServer Faces, a standardised display technology. The MVC design pattern separates model and display, allowing developers to concentrate on their primary competencies and communicate more effectively. The h:selectOneMenu tag creates an HTML input element of type "select" with an unspecified size. A single select HTML input element of type "select" with no specified size is rendered using the JSF h:selectOneMenu tag.
Syntax
Code:
<h:selectOneMenu value = "#{userInfo.data}">
<f:selectItem itemValue = "1" itemLabel = "Item 1" />
<f:selectItem itemValue = "2" itemLabel = "Item 2" />
</h:selectOneMenu>Rendered Output
Code:
<select name = "codingNinjas6:codinNinjas8">
<option value = "1">Item 1</option>
<option value = "2">Item 2</option>
</select>Tag Attributes
The message Tag properties are listed in the tables below:
| S.NO. | ATTRIBUTES |
DESCRIPTION |
title |
A title that is used for accessibility. Browsers often generate tooltips for the value of the title. | |
| 2. | border |
The width of an element's border in pixels. |
| 3. | id |
It is used as a component's identifier. |
| 4. | binding |
The component that can use in a backing bean. |
| 5. | rendered |
It is a boolean tag attribute, where false reduces rendering. |
| 6. | styleClass |
It is used as the class name for Cascading style sheet(CSS). |
| 7. | value | The value of a component, often a value binding. |
| 8. | bgcolor |
It is used to change the background color for the table. |
| 9. | border |
It is used to change the Width of the table’s border. |
| 10. | cellpadding |
It is used to change the Padding around table cells. |
| 11. | cellspacing |
It is used to change the spacing around table cells. |
| 12. | columnClasses |
CSS classes for columns, separated by commas. |
| 13. | columns |
It is used to handle the number of columns in a table. |
| 14. | footerClass |
It is the CSS class for the table footer. |
| 15. | headerClass |
It is the CSS class for the table header. |
| 16. | rowClasses |
CSS classes for columns, separated by commas. |
| 17. | frame |
Valid values for the sides of the frame encircling the table to be drawn are none, above, below, hsides, vsides, lhs, rhs, box and border. |
| 18. | rules |
Specification for cell-to-cell lines; permissible values include groups, rows, columns, and all. |
| 19. | summary |
A summary of the table's purpose and structure as it relates to non-visual feedback such as speech. |
| 20. | dir |
Textual direction Valid values are ltr (left to right) and rtl (right to left) (right to left). |
| 21. | lang |
The attributes and text of an element's base language. |
| 22. | onblur |
The element's focus has shifted. |
23. |
onchange |
The element's value shifts. |
24. |
onclick |
The mouse button is clicked over the element. |
25. |
ondblclick |
The mouse button is double-clicked over the element. |
26. |
onfocus |
The element is highlighted. |
27. |
onkeydown |
The desired key is pressed. |
28. |
onkeypress |
The desired key is pressed and subsequently released. |
29. |
onkeyup |
The desired key is released. |
30. |
onmousedown |
The desired element is selected with the mouse. |
31. |
onmousemove |
The desired element has hovered over with the mouse. |
32. |
onmouseout |
The desired element's area is left by the mouse. |
33. |
onmouseover |
The mouse lands on the desired element. |
34. |
onmouseup |
The desired mouse button is released. |
35. |
onselect |
An input field's text has been selected. |







