Assertions In mocha
- assert.ok is the simplest assertion, which verifies the value's authenticity. you only used this when you don't care about the exact value and simply care that it isn't false.
-
assert.equal performs a weak equality check. assert. strictEqual, on the other hand, is presumably safer because it does a strict equality check.
- assert.deepEqual is quite beneficial. It tests in a recursive manner, so you may use it to validate entire JSON trees, for example. It's worth noting that it employs sloppy equality checking.
-
assert.throws are used to check for errors raised by functions. It executes the provided code and anticipates an exception. You may even specify which exception is thrown by giving a second option.
And there is also the inverse of these which are possible notEqual, notStrictEqual, notDeepEqual, doesNotThrow. They do exactly what you'd expect them to do!
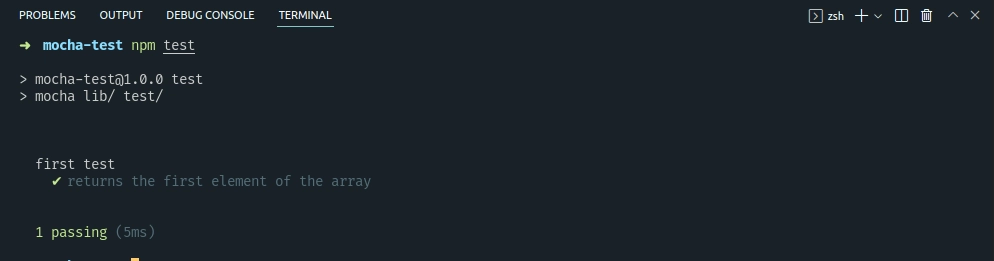
Example of assert.strictEqual
it("returns undefined if array is empty", () => {
var result = first([]);
assert.strictEqual(result, undefined, "maybeFirst([]) is undefined");
});

You can also try this code with Online Javascript Compiler
Example of Async Test with Callback
Program
// create delayedMap.js
function delayedMap(array, transform, callback) {
setTimeout(function () {
callback(array.map(transform));
}, 100);
}
module.exports = delayedMap;

You can also try this code with Online Javascript Compiler
Test Program
// create delayedMapTest.js
const assert = require("assert");
const delayedMap = require("../lib/delayed-map");
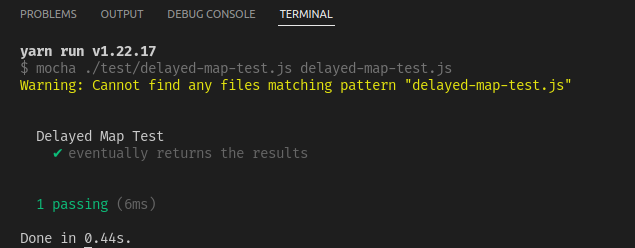
describe("Delayed Map Test", () => {
it("eventually returns the results", function () {
var input = [1, 2, 3];
var transform = function (x) {
return x * 2;
};
delayedMap(input, transform, function (result) {
assert.deepEqual(result, [2, 4, 6]);
});
});
});

You can also try this code with Online Javascript Compiler
Output
Example of Async Test with Promises
Program
// create promise.js
function promiseMap(array, transform) {
return new Promise( function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
resolve(array.map(transform));
}, 100);
});
}
module.exports = promiseMap;

You can also try this code with Online Javascript Compiler
Test Program
// create promiseTest.js
const assert = require("assert");
const promiseMap = require("../lib/promises");
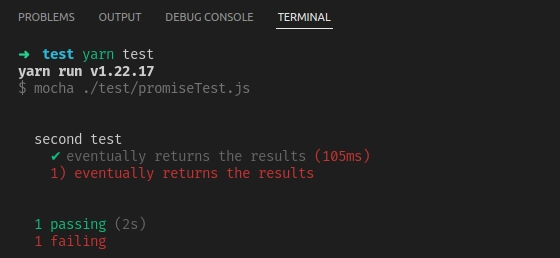
describe("second test", function () {
it("eventually returns the results", function () {
let input = [1, 2, 3];
let transform = function (x) {
return x * 2;
};
return promiseMap(input, transform).then(function (result) {
assert.deepEqual(result, [2, 4, 6]);
});
});
it("eventually returns the results", function (done) {
var input = [1, 2, 3];
var transform = function (x) {
return x * 2;
};
return promiseMap(input, transform).then(function (result) {
assert.deepEqual(result, [2, 4, 6]);
});
});
});

You can also try this code with Online Javascript Compiler
Output
FAQs
-
Does Mocha run tests in parallel?
Individual tests are not executed in parallel by Mocha. That is, if you provide Mocha a solitary, lonely test file, it will create a single worker process, which will run the file. You'll be penalised for using parallel mode if you just have one test file.
-
Is Mocha an assertion library?
Mocha is a JavaScript test framework for Node.js applications that supports browser compatibility, asynchronous testing, reporting on test coverage, and the use of any assertion library.
-
How do you test your promises with Mocha?
If a function produces a promise that you want to assert on the function's outcome, It return the promise in your block for it to work with Mocha. Then you may assert on the promise's outcome in the chain.
-
What is Mocha chai testing?
In a nutshell, Mocha is a Node-based JavaScript test framework that tests coverage reports. Chai is a TDD assertion library for NodeJS and the browser, and it's the next testing tool we'll discuss.Any Javascript testing framework may simply be used with Chai.
Key Takeaways
If you read till here you really enjoyed the article and learned a lot here are few words which summarises the article, A test framework organises the way we create test cases.Mocha is a well-known JavaScript test framework that aids in the organisation and execution of our test cases. On the other hand, Mocha does not examine our code's behaviour. To compare data in a test, use the assert module in Node.js.
You might be interested in articles such as Fundamentals of Software Testing, Running Mocha in Browser, or Mocha Introduction and Feature. Hence never stop your quest for learning. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow. We wish you Good Luck! Keep coding and keep reading Ninja.
Happy Learning!