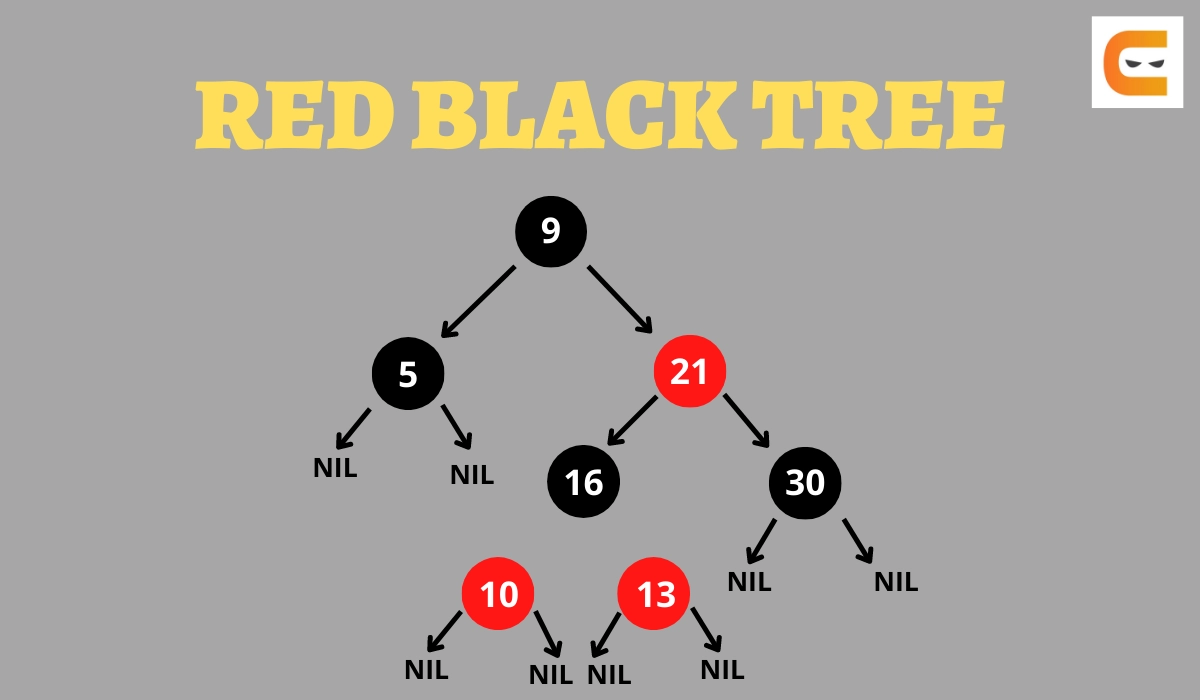
Introduction
In this article, we will learn the basic properties of the AVL and the Red-black trees and the difference between them. They both are the kind of Binary Search Tree and possess properties for self-balancing.
If you don't know about the Binary Search Tree, then don't worry!
A Binary Search tree is a fundamental data structure. It is used to implement other abstract Data Structures like sets, multisets, etc. It is more efficient than a standard binary tree because the operations like searching, insertion, and deletion are performed faster and more efficiently in a binary search tree.
Now coming to the AVL Tree and Red-Black Tree.
Both AVL tree and Red-black tree are widely asked topics in various coding interviews, So let's not get confused between them and understand how they differ from each other.
AVL Tree
Adelson-Velskii and Landis tree (AVL tree) is the kind of binary search tree in which the absolute difference between heights of the left subtree and right subtree must be zero or one.

Before moving further, let’s understand what a balanced factor is.
Balanced Factor
The balanced factor is the difference between the height of the left and right subtree.
Properties
The AVL tree has the following properties:
- The balanced factor of each node should be 0 or -1, or 1.
- Self-balancing binary search tree.
- Re-balancing occurs when the absolute difference between the height of any node's left and right subtree is greater than 1.