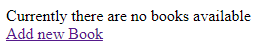Creating View File for Different Methods
There are many methods for creating a view file. And checking in the database whether these actions are valid or not is done by executing the views.
List Method
Create a file named list.html.erb in app/views/book in any editor of your choice. Please refresh your page in the web browser after creating and saving it. Now you must see a blank page. If not, properly check your file name. It should be the same as the controller's method.
Type the following code in list.html.erb:
<% if @books.blank? %>
<p> Currently there are no books available.</p>
<% else %>
<p> Currently these are the books available</p>
<ul id = "books">
<% @books.each do |c| %>
<li><%= link_to c.title, {:action => 'show', :id => c.id} -%></li>
<% end %>
</ul>
<% end %>
<p><%= link_to "Add new Book", {:action => 'new' }%></p>
Explanation
This code checks whether there are any objects in the @books array or not. We used .blank? Method because it returns false if the array is not empty and true if it is empty.
The link_to method call occurs by the code in between <%=%> tags. There are three parameters in link_to. The first one is the text displayed between the <a> tags, and the second one defines the action to be performed when it is clicked. In this case, that is “show,” and the last one is the id of the book passed by params object.
Output
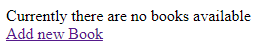
New Method
Create a file named new.html.erb in app/views/book in any editor of your choice. As we do not have any books in our library till now, we will add some. Write the code in your new.html.erb file:
<h1>Add new book</h1>
<%= form_tag :action => 'create' do %>
<p><label for = "book_title">Title</label>:
<%= text_field 'books', 'title' %></p>
<p><label for = "book_price">Price</label>:
<%= text_field 'books', 'price' %></p>
<p><label for = "book_subject_id">Subject</label>:
<%= collection_select(:books, :subject_id, @subjects, :id, :name, prompt: true) %></p>
<p><label for = "book_description">Description</label><br/>
<%= text_area 'books', 'description' %></p>
<%= submit_tag "Create" %>
<% end -%>
<%= link_to 'Back', {:action => 'list'} %>
Explanation
The form_tag interprets the the ruby code into normal HTML <form> tag.
The <input> text field is given by the text_field method. The parameters for the text_field are field name and object.
The collection_select creates HTML select menu. The parameters are as follows:
- :subject_id- When the book is saved, this field is populated.
- : book- The object you are using.
- @books- It is the array you are working within the code.
- : name- The output is visible to users in the output menu.
- : id - It is the value stored in a database.
The submit_tag submits the form. The end here behaves as</form>.
Go to the url: http://localhost:3000/book/new in your browser. The output will be like this.

Enter values accordingly in the form and then click on create button. Here I have added the following details:
Title: Advance Mathematics
Subject: Mathematics
Price: 400
Description: This is test to create new book
Output
When you click on create button, it will redirect you to the page which looks like this:

Show Method
Create a file named show.html.erb in apps/views/book. This method displays the complete detail about all the books available. Write the following code:
<h1><%= @book.title %></h1>
<p>
<strong>Price: </strong> $<%= @book.price %><br />
<strong>Subject :</strong> <%= @book.subject.name %><br />
<strong>Created Date:</strong> <%= @book.created_at %><br />
</p>
<p><%= @book.description %></p>
<hr />
<%= link_to 'Back', {:action => 'list'} %>
Explanation
Here you have pulled the data from the related objects for the first time. In the format @Variable.relatedObject.coloumn format, you are pulling the subject's name value with the help of @ book variable.
Output

Edit Method
Create a file named edit.html.erb in app/views/book in any editor of your choice and write the following code:
<h1>Edit Book Detail</h1>
<%= form_for @book, :url =>{:action => "update", :id =>@book} do |f| %>
<p>Title: <%= f.text_field 'title' %></p>
<p>Subject: <%= f.collection_select :subject_id, Subject.all, :id, :name %></p>
<p>Price: <%= f.text_field 'price' %></p>
<p>Description<br/>
<%= f.text_area 'description' %></p>
<%= f.submit "Save changes" %>
<% end %>
<%= link_to 'Back', {:action => 'list' } %>
Explanation
The code is mostly similar to the new method one, except here we are updating in action rather than creating and defining in it.
For the form action, we used the form_for tag because it performs better than the form_tag as it interacts with the models easily.
Now we are going to modify list method’s like this
<li>
<%= link_to c.title, {:action => "show", :id => c.id} -%>
<b> <%= link_to 'Edit', {:action => "edit",
:id => c.id} %></b>
</li>
Now visit http://localhost:3000/book/list.
Now you can edit this information and save the changes by clicking the save changes button.
Output

Delete Method
In the delete method, you do not require to make a separate view file and write code in that. Here to display the result this metod uses the list method. So we need to modifylist.html.erb and add a delete link.
<li>
<%= link_to c.title, {:action => 'show', :id => c.id} -%>
<b> <%= link_to 'Edit', {:action => 'edit', :id => c.id} %></b>
<b> <%= link_to "Delete", {:action => 'delete', :id => c.id},
:confirm => "Are you sure you want to delete this item?" %></b>
</li>
Explanation
In the delete part, we have used: confirm parameter as it pops up a JavaScript Confirmation box which asks users whether they want to delete or not and if you click on OK, then it proceeds further and deletes the item.
Now visit http://localhost:3000/book/list. It will show the Edit and Delete buttons.
Output

Show_subjects Method
Create a file named show_subjects.html.erb in app/views/book in any editor of your choice and write the following code:
<h1><%= @subject.name -%></h1>
<ul>
<% @subject.books.each do |c| %>
<li><%= link_to c.title, :action => "show", :id => c.id -%></li>
<% end %>
</ul>
Explanation
Now we are iterating through a single subject's many books listings, and with this, we are taking advantage of the association.
Now in show.html.erb we will change the Subject:line as below:
<strong>Subject: </strong> <%= link_to @book.subject.name,
:action => "show_subjects", :id => @book.subject.id %><br />
The list of the subjects will be visible on the index page.
Add the following code in list.html.erb:
<ul id = "subjects">
<% Subject.find(:all).each do |c| %>
<li><%= link_to c.name, :action => "show_subjects", :id => c.id %></li>
<% end %>
</ul>
Now visit http://localhost:3000/book/list. It will show the Edit and Delete buttons.
Output

FAQs
-
What do rails mean in Ruby on Rails?
Rail is a framework used for building web applications.
-
What is the role of the subdirectory app?
They find the controller classes.
-
Mention some of the aspects of Rails?
They provide many features like Meta-programming, Convention over configuration, etc.
-
Why do we need a view?
To continuously change the database's tables.
Key Takeaways
In this blog, we have learned about views, their role in ruby on rails, and different methods to create them like list method, show_subject method, new method, etc., and also learned how to delete them.
If you want to learn about Ruby on Rails on a brief level, then you should refer to this blog. This will give you a complete idea about its advantages and other stuff.
Also check out - Strong Number