Types of Decision Making Statements in R
In R, there are several types of decision-making statements that allow you to control the flow of your program based on different conditions. The commonly used decision-making statements in R are:
if statement:
The if statement allows you to execute a block of code if a specified condition is true. If the condition is false, the code block is skipped.

The basic syntax of the if statement is as follows:
Syntax
if (condition) {
# Code to be executed if condition is true
}
Code Example
message <- TRUE
if (message) {
print("If statement got executed")
}
Output
[1] "If statement got executed"
Let us modify this code by making the message variable = FALSE to see the result.
Modified Code
message <- FALSE
if (message) {
print("If statement got executed")
}
Output
No Output
From the output itself it is very clear that to execute a block of code the if statement has to be true. By using this powerful concept, we can make our code more efficient.
The next statement is if-else statement:
if-else statement:
The if-else statement extends the functionality of the if statement by allowing you to execute one block of code if the condition is true and another block of code if the condition is false.
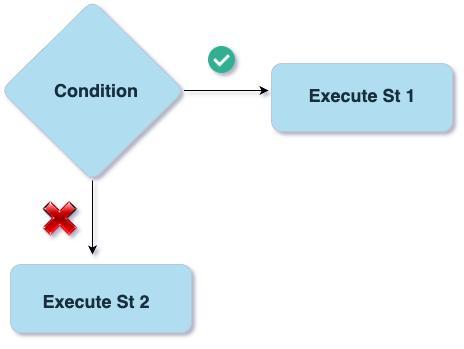
The basic syntax of the if-else statement is as follows:
Syntax
if (condition) {
# Code to be executed if condition is true
} else {
# Code to be executed if condition is false
}
Code Example
message <- FALSE
if (message) {
print("If statement got executed")
} else{
print("else statement got executed")
}
Output
[1] "else statement got executed"
In the example above, the message contains the FALSE value, hence it falls under the else part.
Next-up let us see if we can add multiple conditions in the program or not.
if-else if-else statement:
The if-else if-else statement, also known as the "else if ladder," is used when you have multiple conditions to check. It allows you to test multiple conditions one by one and execute the corresponding code block of the first condition that evaluates to true.

The basic syntax of the if-else if-else statement is as follows:
Syntax
if (condition1) {
# Code to be executed if condition1 is true
} else if (condition2) {
# Code to be executed if condition2 is true
} else {
# Code to be executed if all conditions are false
}
Code Example
num <- 12
if (num < 0) {
print("number is negative")
} else if (num == 0) {
print("number is zero")
} else {
print("number is positive")
}
Output
[1] "number is positive"
You can try passing different input to see the working of if-else if-else statement.
switch statement:
The switch statement allows you to select one of several code blocks to execute based on the value of a specific expression. It is useful when you have a single expression with multiple possible values and you want to execute different code blocks based on those values.

The basic syntax of the switch statement is as follows:
Syntax
switch(expression,
value1 = {
# Code to be executed if expression matches value1
},
value2 = {
# Code to be executed if expression matches value2
},
default = {
# Code to be executed if expression doesn't match any value
}
)
Code Example
day <- "wednesday"
result <- switch(day,
"monday" = {
# Code for case "monday"
"Result for Monday"
},
"tuesday" = {
# Code for case "tuesday"
"Result for Tuesday"
},
"wednesday" = {
# Code for case "wednesday"
"Result for Wednesday"
},
"thursday" = {
# Code for case "thursday"
"Result for Thursday"
},
# Default case
{
# Code for default case
"Result for default case"
}
)
print(result)
Output
[1] "Result for Wednesday"
These decision-making statements in R provide you with the flexibility to control the program flow based on different conditions and make your code more dynamic and responsive.\
Using Logical Operators in Decision Making in R
In R, logical operators are commonly used in decision-making statements to evaluate multiple conditions. The two primary logical operators are && (logical AND) and || (logical OR).
Logical AND (&&):
The && operator is used to check if multiple conditions are all TRUE.
It returns TRUE only if all the conditions are TRUE; otherwise, it returns FALSE.
Example:
x <- 5
y <- 10
if (x > 0 && y > 0) {
print("Both x and y are greater than 0.")
}
Output
[1] "Both x and y are greater than 0."
Logical OR (||):
The || operator is used to check if at least one of the conditions is TRUE.
It returns TRUE if any of the conditions is TRUE; otherwise, it returns FALSE.
Example:
x <- 5
y <- 10
if (x > 0 || y > 0) {
print("Either x or y (or both) is greater than 0.")
}
Output
[1] "Either x or y (or both) is greater than 0."
Frequently Asked Questions
What is R programming language?
The R programming language allows you to analyze data, machine learning, data science models, etc. It helps you create and modify packages, functions, etc. It is an open-source programming language. It is in high demand nowadays.
What are the advantages of the R programming language?
It is an open-source programming language compatible with other languages. It is independent of the platform it is being used on. It offers several packages for data analysis. It is also used for machine learning algorithms, data science, etc.
Is R language in demand today?
R programming language is trendy among data scientists and analysts because it helps them import and clean their data to perform analysis. Also, many companies use the R language.
What is the purpose of the ifelse() function in R, and how does it differ from if-else statements?
The ifelse() function in R is designed to provide a vectorized approach to conditional statements. It allows you to apply a condition to each element of a vector or a set of vectors and return a corresponding value based on the outcome of the condition.
Conclusion
In this article, we studied decision making statements in R and its types, along with some significant examples using R language. We have also discussed some frequently asked questions based on the same.
If you want to dive deep into the knowledge pool of R programming language, do read the following:-
To learn more about DSA, competitive coding, and many more knowledgeable topics, please look into the guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio. Also, you can enroll in our courses and check out the mock test and problems available. Please check out our interview experiences and interview bundle for placement preparations.
Happy Coding!










