Introduction
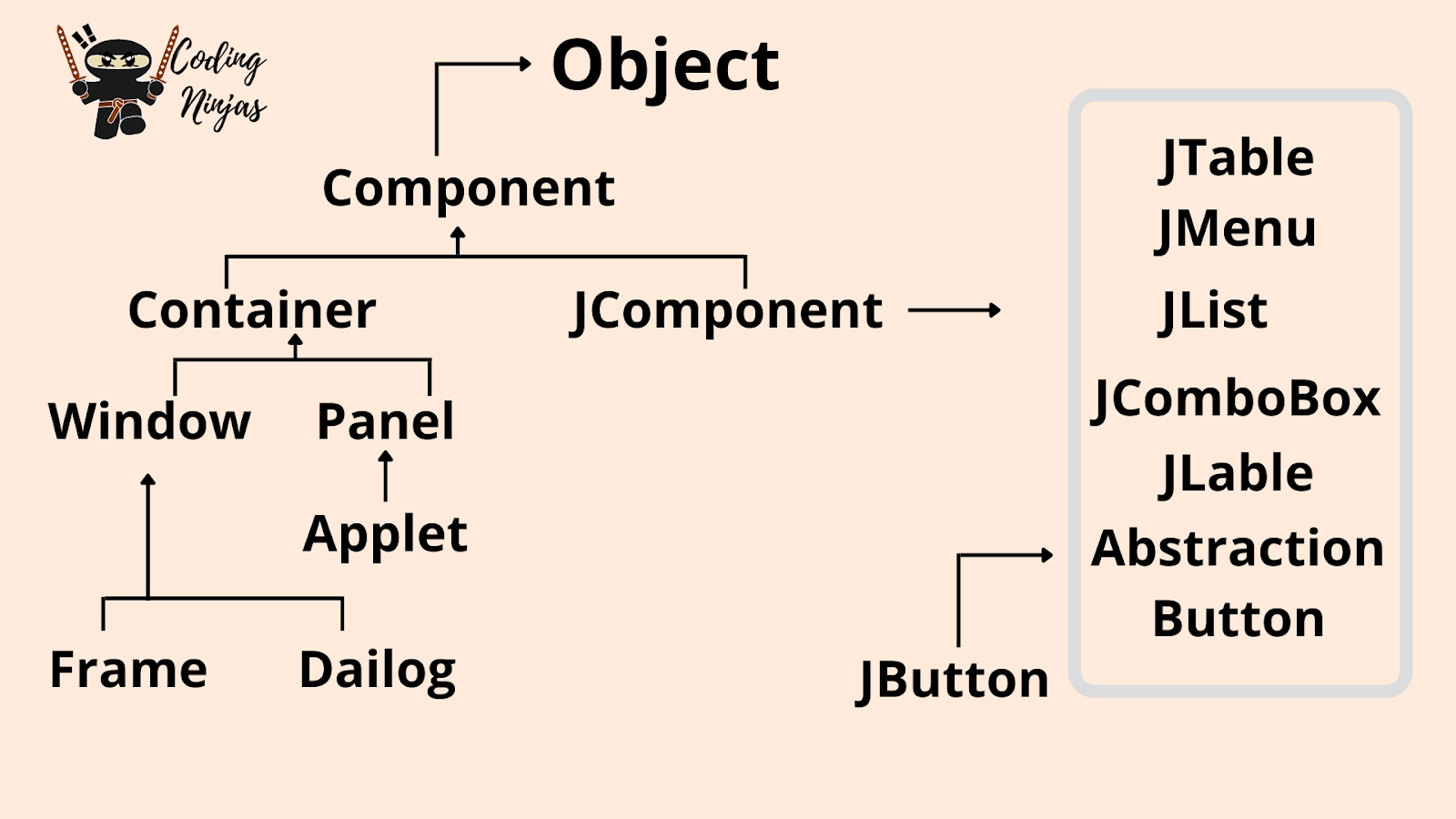
Swing in Java is a lightweight and platform-independent class of the Java foundation class. It's used to make applications that run on Windows. It contains elements such as a button, a scroll bar, and a text field. A graphical user interface is created by combining all of these elements. In this article, we'll go over the concepts and features of the Java Swing Framework includes several classes that provide more vital and more versatile GUI (Graphical User Interface) components than AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit).

Swing is a Sun Microsystems-published official Java GUI toolkit that closely resembles the look and feels of modern Java GUIs. It is used to create the graphical user interface for Java Class.
The concepts discussed in this article are as follows:
Recommended Topic: Fibonacci Series in Java
Features of Java Swing
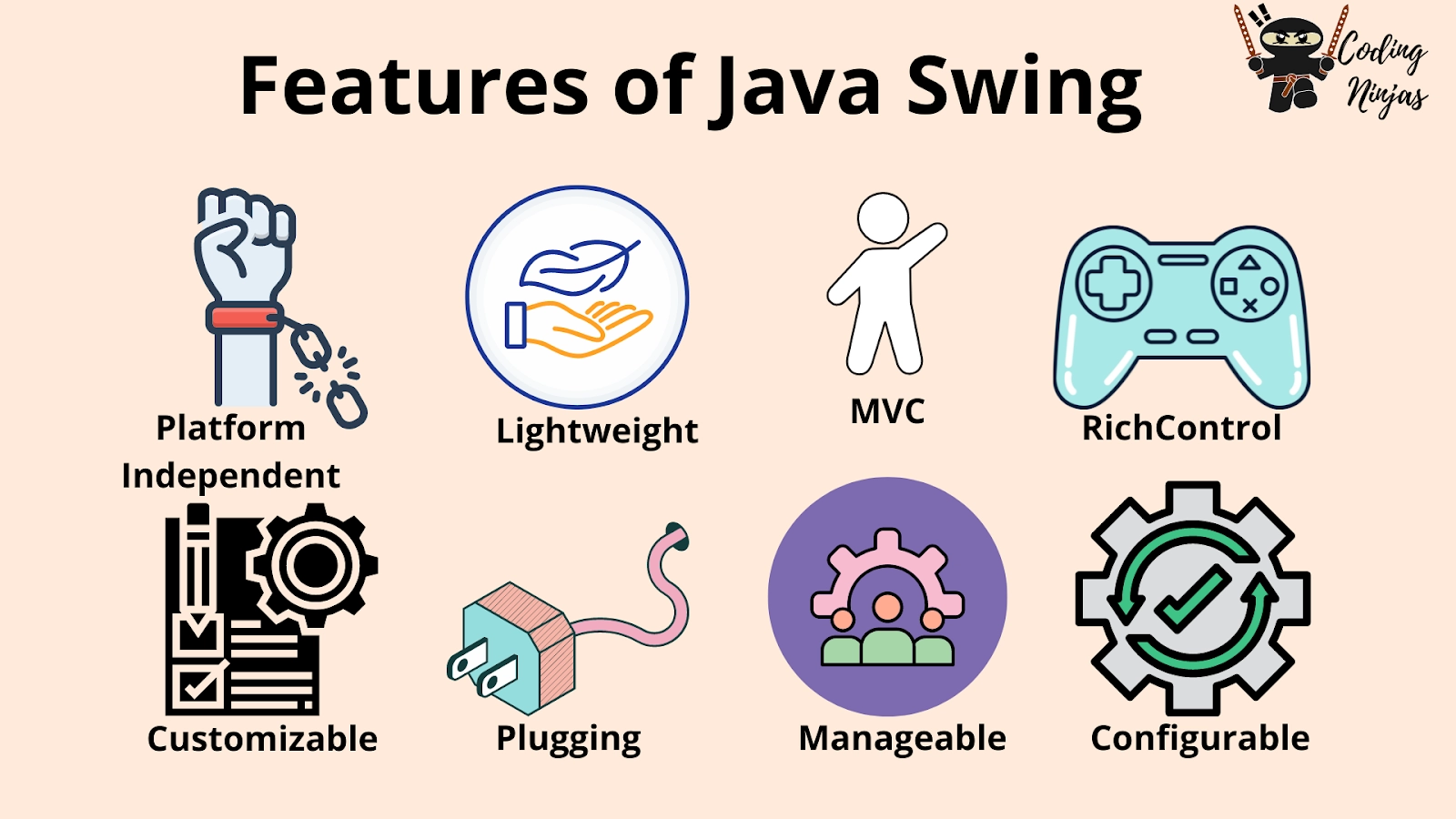
- Platform Independent
- Customizable
- Plugging
- MVC
- Manageable Look and Feel
- Lightweight
Let's learn about these features in detail:
1. Platform Independent
It is platform-independent, as the swing components used to construct the program are not platform-specific. It works on any platform and in any location.
2. Customizable
Swing controls are simple to customize. It can be changed, and the swing component application's visual appearance is independent of its internal representation.
3. Plugging
Java Swing has pluggable look and feel. This feature allows users to change the appearance and feel of Swing components without having to restart the application. The Swing library will enable components to have the same look and feel across all platforms, regardless of where the program is running. The Swing library provides an API that allows complete control over the appearance and feel of an application's graphical user interface.
4. MVC
The MVC Relationships:
A visual component is made up of three distinct aspects in general:
- The appearance of the component when it is rendered on the screen.
- The component responds to the user.
- The state information connection with the component.
One component architecture has proven to be exceptionally effective over time.
MVC stands for Model-View-Controller.
- The model agrees with the state information associated with the Component in MVC terminology.
- The view determines how the component appears on screen and any aspects of the view that are influenced by the model's current state.
- The controller is in charge of determining how the component responds to the user.
5. Manageable Look and Feel
It's simple to manage and configure. Its mechanism and composition pattern allows changes to be made to the settings while the program runs. Constant changes to the application code can be made without making any changes to the user interface.
6. Lightweight
Lightweight Components: The JDK's AWT has supported lightweight component development since version 1.1. A component must not rely on non-Java [O/s based] system classes to be considered light. The look and feel classes in Java help Swing components have their view.
You can also read about Why is Java Platform Independent here.
7. Rich Control
Swing offers a wide variety of rich, interactive controls such as buttons, text fields, tables, sliders, and trees. These components enable the creation of sophisticated user interfaces with advanced features like drag-and-drop support, tooltips, and event handling, enhancing user interaction.
8. Configurable
Swing allows extensive configuration of its components. Developers can set properties such as size, color, font, and event handling, and even define custom behaviours for components. This configurability ensures that the GUI can adapt to various application requirements and user preferences.