Introduction
Salt is an open-source software used to manage software configuration and to perform remote execution of commands. Salt allows us to manage hundreds, or even thousands of servers using very few (could even be one) Master nodes. File servers are an integral part of Salt - they are used to efficiently deliver files to Minion nodes.

This article will cover the steps to set up and configure your file server using Salt. You'll learn how to use Salt's powerful configuration management and automation capabilities to quickly and easily deploy and manage your file server.
Salt File Servers
Salt File Servers are written in ZeroMQ. ZeroMQ is a messaging library. It allows us to send messages between different processes and different servers. It is exceptional in the fact that it doesn't use any message broker - i.e., no particular middleware is used for handling the messages. This makes it fast, efficient, and easy to use.
Basic Setup
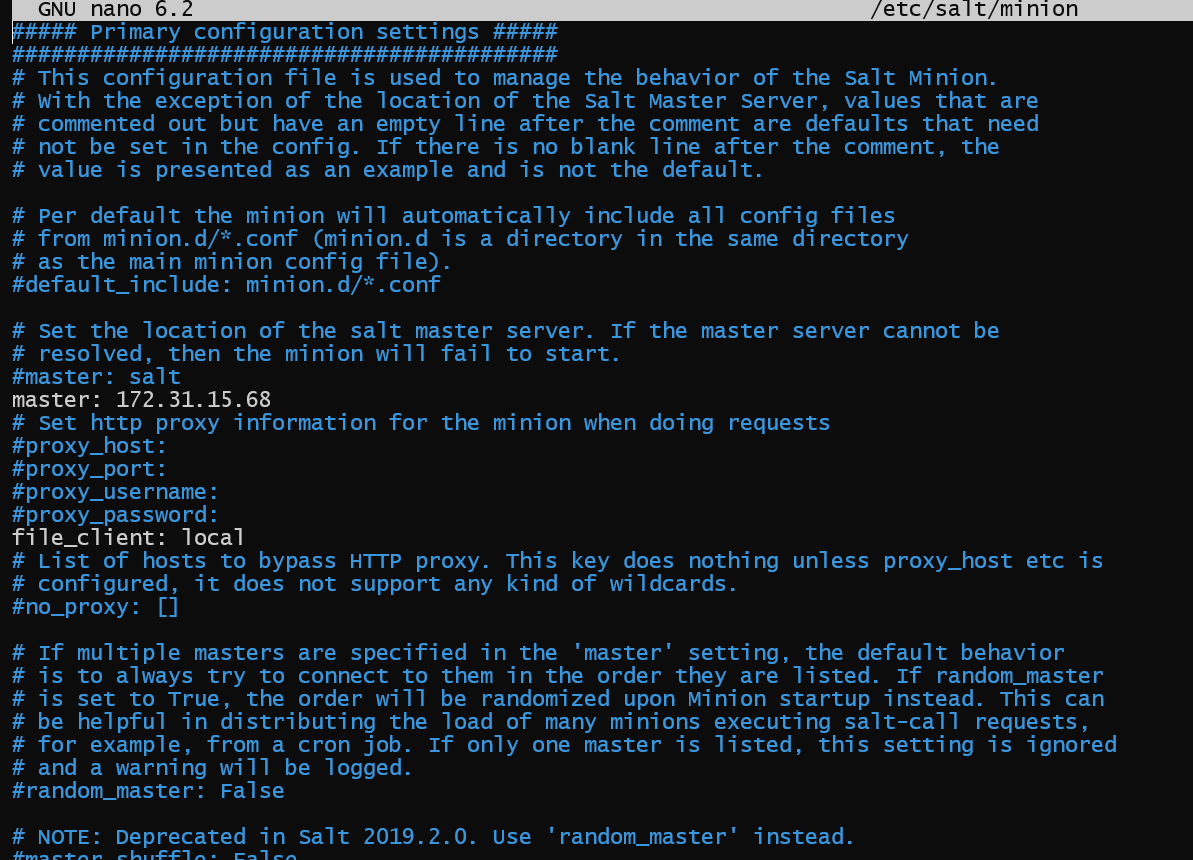
To perform the basic setup, go to the master config file. It is usually present at /srv/salt/master on the master machine. Add the following lines to it.
file_roots:
base:
- /srv/salt
We will see the meaning of this in the coming paragraphs.
Environments
Most software development processes use the concept of environments. For example, the coding part generally occurs in the dev environment. There is a separate test environment for testing, staging, and, finally production. Different organizations may have more or fewer environments, and they may be named differently.
Then, it makes sense to have environments in our Salt file server configuration. Different environments would need different files. Salt allows us to add environments to our file servers. This lets each environment have different file trees.
We can specify different environments in the following way.
file_roots:
base:
- /srv/salt/base
dev:
- /srv/salt/dev
prod:
- /srv/salt/prod
With this configuration, Salt will look for a particular file in whatever environment is currently being used.
For example, say we search for a file named test.txt, a dummy text file. If we are working in the base environment, Salt will look in /srv/salt/base on the master machine. On the other hand, Salt will look in the /srv/salt/dev folder if we are working in the dev environment. We can specify which environment we are in when running salt commands.
Directory Overlay
Sometimes, we cannot guarantee that a particular file will be in a particular folder or it might not exist in a particular environment. We can use Salt's directory overlay feature to avoid error responses in these cases.
With these, we can add multiple directories for each environment. They will be searched in the order that they are listed.
file_roots:
base:
- /srv/salt/base
- /srv/salt/other_folder
dev:
- /srv/salt/dev
- /srv/salt/dev_other
- /srv/salt/base
prod:
- /srv/salt/prod
- /srv/salt/prod_other
- /srv/salt/base
Searching for files will follow this flowchart.
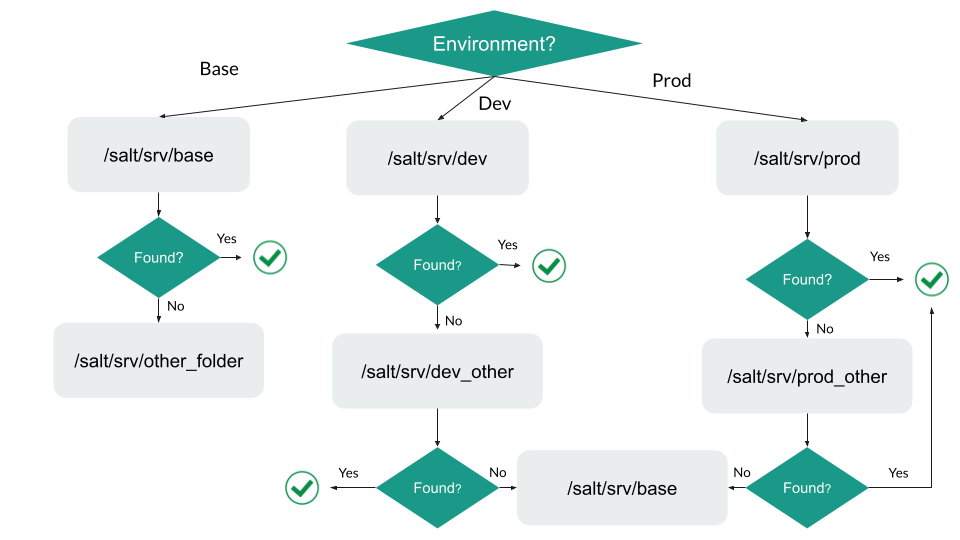
If the file is not found even in the last folders, Salt will be unable to deploy it across minion machines.