Introduction
A system architecture is a model showing various components' functionality, mapping and user interaction. One can use it to assist in designing a composite system. A system architecture involves hardware and software components.

In this article, we will cover Salt System Architecture, the components of System Architecture in detail and the states of the Salt System Architecture.
Salt System Architecture
Any number of servers, even those in local network systems and other deployments distributed across many data centres, can operate with SaltStack's architecture. A Salt master issues command to a Salt client, who then carries them out. This is known as the master-client model.
The following diagram shows the Salt System Architecture:
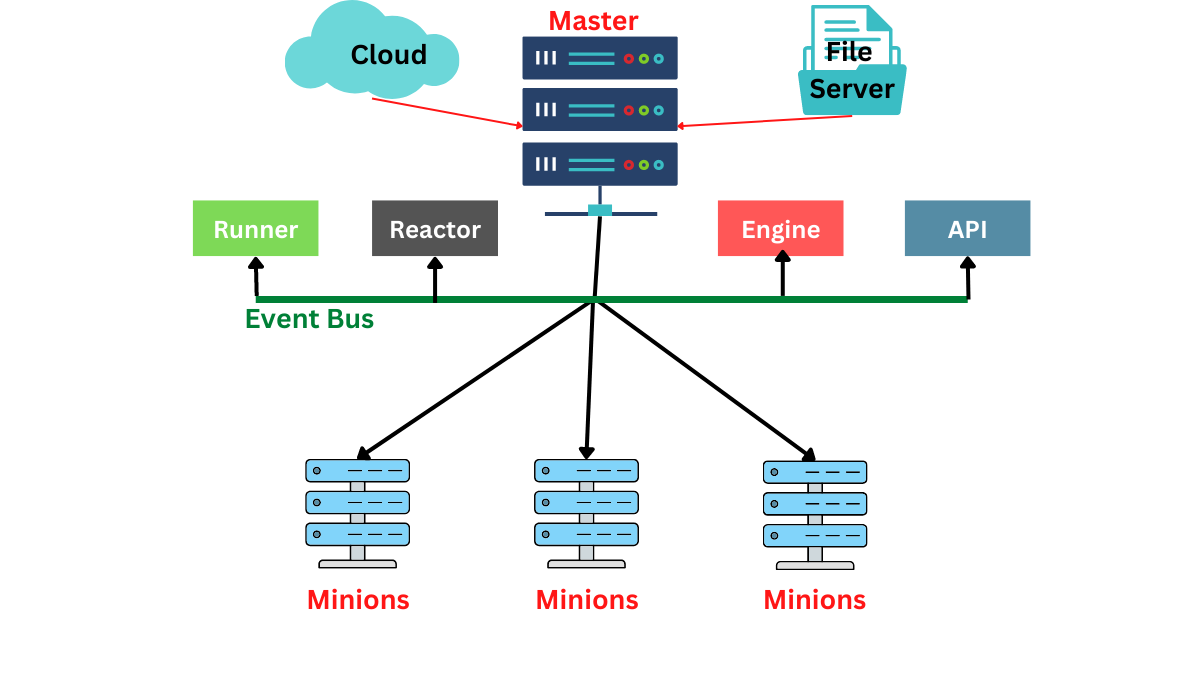
We will discuss each component in detail.
Masters and Minions
The Salt Master is a server that manages the salt-master service in the Salt system. It sends instructions to one or more Salt Minions. Minions are also servers that are registered with that specific Salt Master and are used to conduct the salt-minion service.
Salt can also be viewed as a publisher-subscriber model. Salt Minions subscribe to the jobs that the master publishes and that needs to be done. It will carry out a specific job when it applies to that minion.

A minion returns the job result to the master after completing its assigned task. For the minions to connect with their master by default, Salt uses two ports. The main task of these two ports is to receive and send data to the Message Bus. ZeroMQ is the networking layer of Salt or Salt's message bus. It builds an asynchronous network topology to provide the quickest communication possible.
Event Bus
The Salt Master and Salt Minions communicate using the event system. The main uses of event systems are as follows:
-
Both the master and the minions are aware of events.
-
Both can keep a close watch on events and analyse them.
The features of event systems are as follows:
-
Real-time Monitoring.
-
Pluggable System.
-
Flexible Transport Layer using ZeroMQ.
-
Complete TCP-based transport layer using Tornado.
- Efficient.
Targets and Grains
By defining a target, the master tells the minions which should perform the task. A target is the collection of minions under the control of one or more masters to which a job's Salt command is applied.
Grains are defined as shared system features or other custom attributes. Although grains can be defined in various methods, they are always derived from or defined on the minion. Some examples of grains are as follows:
-
OS type.
-
Domain name.
-
IP address.
-
Kernel.
-
Memory.
These traits are used to target the minions by the Master Server.
The master can target the minions in various ways:
-
Using the command.
-
Using the specific IDs.
-
Using the shared traits(grains).
The following is an example of one of the many different types of orders that a master may give to a minion using commands.
salt -v '*' pkg.install <app_name>
Here, the glob( '*') is the target.
Runners and Reactors
The salt-run command executes convenience programmes known as salt runners. Salt execution modules and Salt runners both function similarly. Instead of the Salt Minions, they execute the Salt Master. A Salt runner can be a basic client call or a complex programme.
Reactors can be used in various situations, such as
-
The Scalability of the infrastructure.
-
Automatic Rollback.
-
Administrator notification.
-
Restarting unsuccessful programs.
Salt can start actions in reaction to an event thanks to its Reactor mechanism. It provides a simple interface for monitoring Salt's system event bus for event tags that fit a specified pattern and executing one or more actions. This system links SLS files to event tags on the master.
SLS files stand for Salt State files. The SLS is designed to contain all information in a simple format and depicts the state in which a system should be. You can specify how your systems should function using these files, including the installed and active apps and services.





