Introduction ⛳
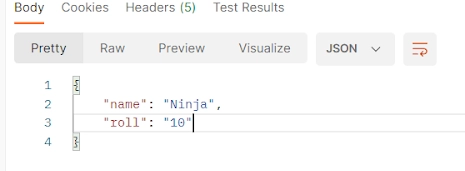
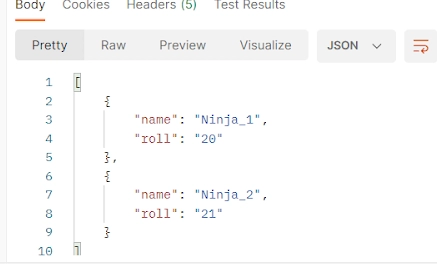
A REST or RESTful API is an acronym for Representational State Transfer API. It is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints to create web services and is one of the most common choices in terms of public APIs. It uses HTTP to send a request from a client to a server, and the response is received in the form of HTML, XML, JSON (the most popular format), or image.

In this blog, we will discuss swagger and RESTful services with Spring Boot.
Enhancing Swagger Documentation with Custom Annotations📝
Swagger is an open-source tool and builds around OpenAPI Specification. It is helpful for developers to design, develop and use RESTful APIs. Swagger supports JSON and UI, making it one of the most popular API documentation formats for RESTful Services.
The main Swagger tools are:
⭕Swagger UI: helps in creating interactive API documentation.
⭕Swagger Editor: browser-based editor to write OpenAPI specifications.
⭕Swagger Codegen: generates client libraries and server stubs(API implementation stub) from OpenAPI specification.
Let us first generate Swagger documentation for RESTful services.
STEPS :
▶ Download the Spring Tool Suite(STS) and create a starter project.
▶ Add the dependencies springfox-swagger2 and springfox-swagger-ui in pom.xml file.
The dependencies are as follows-
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency> ▶ Now, create a class with the name ConfigureSwagger.java and write the following code :
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
//Enable Swagger
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig
{
//creating bean
@Bean
public Docket api()
{
//creating constructor of Docket class that accepts parameter DocumentationType
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2);
}
}
▶ Run the application and open the browser having URI as http://localhost:8080/v2/api-docs
The above link will show a JSON format Swagger documentation.
Here are the main steps for Enhancing Swagger Documentation
STEPS:
▶ In the ConfigureSwagger.java file, make a constant DEFAULT_API of type ApiInfo.
private static final ApiInfo DEFAULT_API = null;
▶ Hold the ctrl key and then click on ApiInfo, which will open the ApiInfo class. The ApiInfo class will look like this :
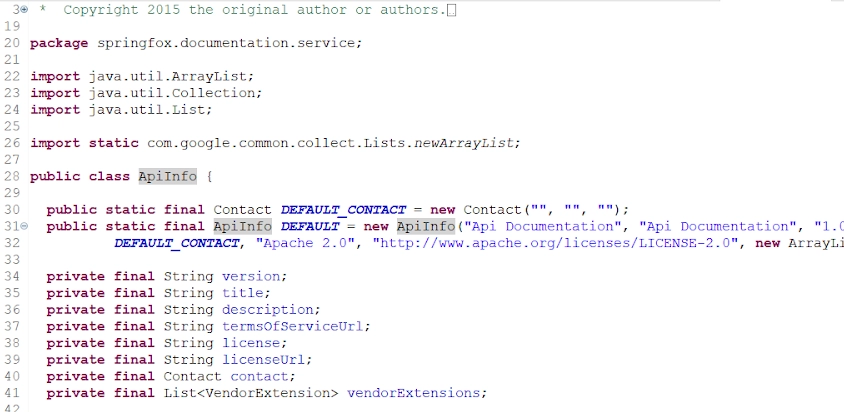
▶ Copy the constants DEFAULT_CONTACT and DEFAULT as in the class ApiInfo and paste them into the ConfigureSwagger.java class. Rename the constant DEFAULT to DEFAULT_API.
▶ Configure the DEFAULT_API and contact details(DEFAULT_CONTACT ) of the developer or organization.
The final ConfigureSwagger will look like this
package com.example.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.service.VendorExtension;
@Configuration
//Enable Swagger
@EnableSwagger2
public class ConfigureSwagger {
public static final Contact DEFAULT_CONTACT = new Contact("Ninja", "https://www.codingninjas.com/", "example@codingninjas.com");
public static final ApiInfo DEFAULT_API = new ApiInfo("Example RESTful Api", "Api Documentation", "1.0", "urn:tos", DEFAULT_CONTACT, "Apache 2.0", "http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0", new ArrayList<VendorExtension>());
@Bean
public Docket api()
{
ApiInfo apiInfo;
//creating constructor of Docket class that accepts parameter DocumentationType
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(DEFAULT_API);
}
}▶ Restart the application, and in the browser, go to the URI http://localhost:8080/v2/api-docs. It will show the updated API and contact detail in the Swagger documentation