Introduction
A Java specification called JPA (Java Persistence API) is used to manage and persist data across Java objects and relational databases. It is regarded as the industry-standard methodology for object-relational mapping.
JPA illustrates how to define a POJO (Plain Old Java Object) as an entity and maintain relations with it using specific meta settings.
Hibernate is a free, open-source ORM (Object Relational Mapping) solution that offers any Java application Object-Relational persistence and query service. It implements the Java Persistence API, one of the most used ones. Because Java objects can be more readily mapped to databases, common persistence-related programming tasks are made more accessible.
This blog will look at all the points of JPA vs. Hibernate.
Features
Let us discuss some of the key features of JPA vs. Hibernate.
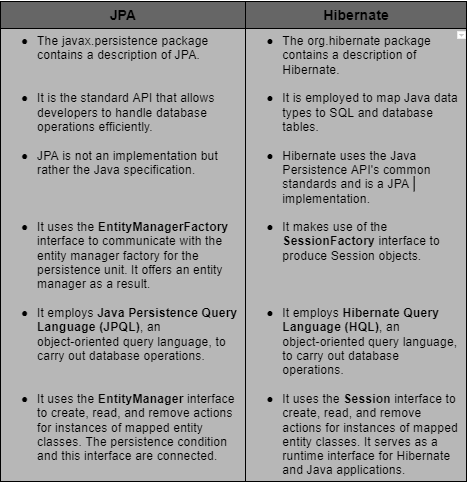
JPA
- JPA supports pluggable third-party persistence providers like Hibernate and Toplink.
- A model class can employ annotation defaults, which expedites development and reduces costs.
- JPA enables you to create a vendor-neutral persistence layer that supports any persistence provider.
- Additionally, the JPA application can be set up to create a database schema based on the persistence model.
- Switching to the best-performing persistence provider is likewise reasonably simple. Moving to any commercial persistence provider is simple.
- JPA enables polymorphic queries, polymorphism, and inheritance.
- JPA supports both static and dynamic queries.
Hibernate
- For developers to utilize and incorporate into their Java applications, Hibernate is open-source software for which the source code is available.
- Hibernate has a capability that automatically creates the database table, and programmers don't have to worry about how to implement queries. Hibernate operates independently.
- Hibernate adheres to the inheritance principle.
- One-to-one, one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships are all supported by the Hibernate framework.
- Hibernate offers a slow loading capability; utilizing this idea only fetches the essential objects for execution, improving application efficiency.