Introduction
Kivy is a multi-platform Python GUI development library that runs on iOS, Android, Windows, OS X, and GNU/Linux. It aids in the development of apps that make use of cutting-edge multi-touch user interfaces. Kivy's core concept allows developers to create an app once and deploy it across all devices, making code reusable and deployable and enabling quick and easy interaction design and prototyping.
In this article with the help of a few examples, we'll look at how to implement the Stacklayout widget in Kivy Python. This post assumes you've done some Python programming before. If that is not the case, you can return here after reading our Basics of Python article.
Stack Layout
StackLayout assists us with vertical and horizontal button placement. Because the sizes of all buttons in StackLayout do not need to be the same, we can arrange them as we want. There are four row-wise and 4 column-wise orientations.
To use StackLayout, first import it using the command below:
from kivy.uix.stacklayout import StackLayoutStackLayout Orientation (2D):
-right to left or left to right
- top to bottom or bottom to top
- 'rl-bt', 'rl-tb', lr-bt', 'lr-tb'(Row wise)
- 'bt-rl', 'bt-lr', 'tb-rl', 'tb-lr'(Column wise)To use FloatLayout, you must have to import :
1) import kivy
2) import kivyApp
3) import Button
4) import Stacklayout
5) Set minimum version(optional)
6) Create the StackLayout class
7) Create the App class
8) Set up .kv file (name same as App class)
9) return StackLayout Class
10) Run an instance of the classImplementing StackLayout:
Now we'll look at a sample python application code that uses Kivy to show how the approach described above for stackLayout works.
main.py file
import kivy
kivy.require('1.11.1')
# program to show how to use StackLayout using .kv file
# base Class of your App inherits from the App class.
# app:always used to refers to the instance of your application
from kivy.app import App
# The StackLayout arranges children vertically
# or horizontally, as many as the layout can fit.
from kivy.uix.stacklayout import StackLayout
# creating the root widget used in .kv file
class MyStackLayout(StackLayout):
pass
# class in which name .kv file must be named Slider.kv.
# or creating the App class
class StackApp(App):
def build(self):
return MyStackLayout()
# run the app
if __name__ == '__main__':
StackApp().run()The.kv file must have the same name as the App class, for example, Stack.kv.
.kv file
#.kv file for implementation of StackLayout
# Different orientation
# ['tb-rl', 'lr-tb', 'tb-lr', 'rl-tb', 'lr-bt', 'bt-lr', 'rl-bt', 'bt-rl']
<MyStackLayout>:
orientation: 'lr-bt'
Button:
text: '0'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '1'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '2'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '3'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '4'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '5'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '6'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '7'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '8'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Button:
text: '9'
size_hint: (None, None)
size: 100, 100
Output

This is for the 'lr-tb' orientation. The widgets are added from left to right, then from top to bottom.
Note: To alter the orientation, simply modify the orientation on line 04 of the.kv file to one of the following —
For row wise orientation use:
-'lr-tb'
-'lr-bt'
-'rl-tb'
-'rl-bt'
For column wise orientation use:
-'tb-lr'
-'tb-rl'
-'bt-lr'
-'bt-rl'All of the above orientations output are given below
For row wise orientation use:
'lr-tb'
Output

'lr-tb'Output

'rl-tb'
Output
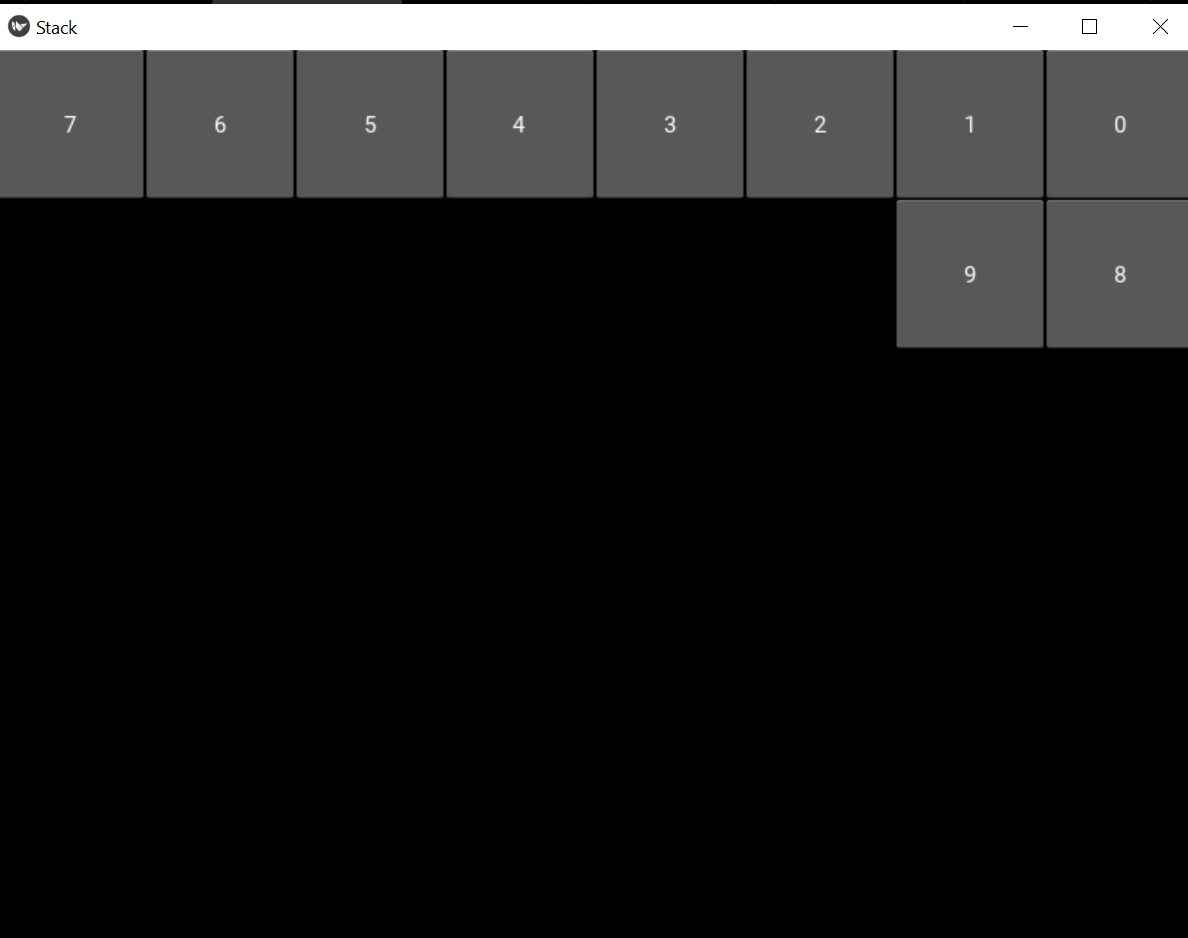
'rl-bt'Output

For column wise orientation use:
'tb-lr'Output

'tb-rl'Output

'bt-lr'Output

'bt-rl'Output





