Introduction
There are very famous Natural Language Processing libraries such as NLTK, spaCy, etc. They are very relaxed and have their merits, but Gensim has some unique features.
Gensim is super fast as it is written so that its code is highly optimised and parallelized, and most of the routine is C routine. Further, Gensim can process arbitrarily large corpora using data stream algorithms. Gensim has no platform dependents. Gensim runs on Linux, Windows, Mac OS, and any other platform, including Python and NumPy. In further discussion, we will be using the Gensim library to build a word2vec model. Let's get started with the implementation part.
Implementation
We will be using Amazon product reviews for cell phone accessories and building word2vec models in a Gensim library. Gensim library is an NLP library in Python, and it's straightforward to use. The syntax is brief compared to TensorFlow, so we will use this and train a model.
Let's first install the Gensim library. We can do PIP install gensim. In Google collab, they provide these inbuilt features, so we don't need to download it explicitly. We need to install another module called python-Levenshtein.
# !pip install gensim
# !pip install python-Levenshtein
import gensim
import pandas as pdAfter importing Gensim and Pandas, I am downloading the Amazon product review data set, and these are the product reviews, especially for cell phones accessories categories. You can get the data from here. It has a huge file and has JSON records with all product reviews, and Pandas supports reading JSON files. Now, We are going to create a data frame.
df = pd.read_json("Cell_Phones_and_Accessories_5.json", lines=True)Let's print a couple of rows of the data frame..
print(df)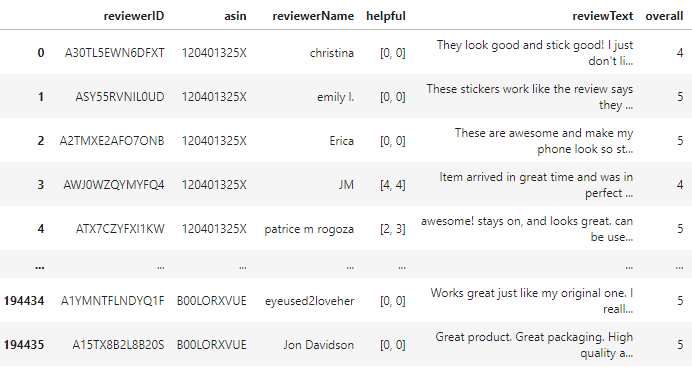
Here we can see the columns as reviewer ID, reviewer name and text, etc. We will train a word2vec model for the cell phone accessories using only a review text. The remaining columns are not helpful to us.
Let's know the shape of the data frame.
df.shape
(194439, 9)We have 194 thousand records; that's a lot of data. That kind of data set is enough to train our model.
The first step of training our word2vec model is preprocessing because these texts have things like stop words, and we don't want these. We want to convert this word into lowercase to know everything is lowercase and comparable, then remove the trailing spaces and punctuation marks. All of these things can be done using a function in Gensim. Gensim library has 'utils.py simple preprocess' that will process these texts.
review_text = df.reviewText.apply(gensim.utils.simple_preprocess)
print(review_text)

We can see it is tokenizing the sentences, meaning that all uppercase letters are converted into lower case letters, and punctuation marks and stop words are removed. By the way, it is not very perfect, and it uses simple heuristic rules for doing this preprocessing. But this is good enough to build our word2vec model. If we want to do the same thing for the entire column, we can do the 'apply' function in the review text. It's going to return to a new Pandas series.
model = gensim.models.Word2Vec(
window=10,
min_count=2,
workers=4,
)Now we will initialize the Gensim model. Gensim is an NLP library, and it comes with the word2vec class. Now I am going to create this model using a couple of parameters. The first parameter is a window that is equal to 10. Here 10 means ten words before the target word and ten words after the target word. We can also experiment with size, and there is no fixed rule; we can even make it 5. Another parameter called mean count is that if we have a sentence with only one word that doesn't use that sentence, at least two words need to be present in the sentence to be considered for the training. 'Workers' is the number of CPU threads we want to use between the models.
Now we need to build a vocabulary. Building a vocabulary means making a unique list of words..
model.build_vocab(review_text, progress_per=1000)To perform the actual training, we will do 'model.train.' It will take a couple of parameters; review the text, and then real examples that tell the real examples we have. The training may take time depending on the computer's CPU, GPU, etc.
model.train(review_text, total_examples=model.corpus_count, epochs=model.epochs)I will save the model in a file because we train a model, save it to a file, and then use a pre-trained model in most locations.
model.save("./word2vec-amazon-cell-accessories-reviews-short.model")There is a product review, and someone says the word 'bad,', and we want to know what the word is similar to bad?
model.wv.most_similar("bad") 
We can see these words are similar to bad following the similarity scores.




