Introduction
As we all know, microoperations in digital computers are Arithmetic, Logic, and shift micro-operations. These all microoperations are performed on digital circuits. If the individual circuit has to be designed for each micro-operation, it will be difficult to manufacture and manage different circuits simultaneously. It will also increase the cost of manufacturing. Due to all these reasons, all the micro-operations are integrated into one circuit, ALSU, which is our discussion for today.
Computer systems have several storage registers connected to a common operational unit called an Arithmetic Logic Unit, ALU.
To perform a micro-operation, the contents of specified registers are placed in the inputs of the common ALU. The ALU performs operations, and results are transferred to the destination register. In ALU, the entire register transfer operation from the source registers to the destination registers can be performed during one clock pulse period.
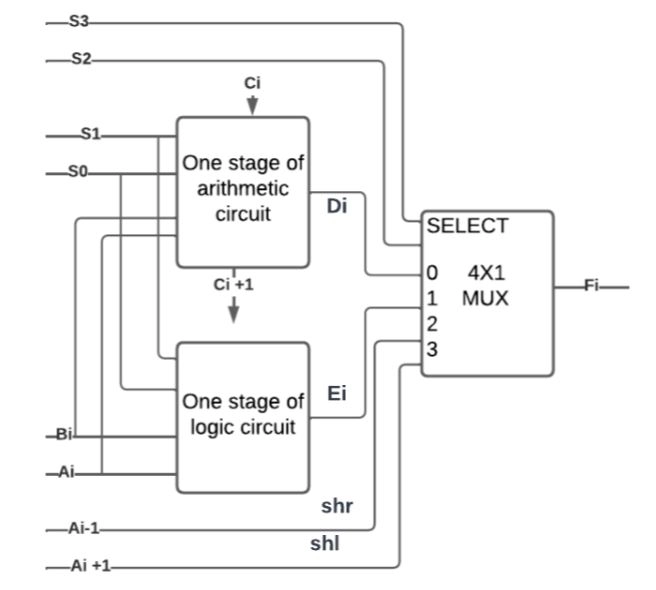
The shift micro-operations are often overall in a separate unit, but sometimes the shift unit is made part of the overall ALU too; this unit is called Arithmetic Logic Shift Unit.
Read About - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics
Arithmetic Logic Shift Unit
The Arithmetic Logic Shift Unit(ALSU) is part of a computer system's Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU). It can be defined as a digital circuit that performs arithmetic, logical, and shift operations. Instead of having individual registers performing microoperations directly, computer systems employ many storage registers connected to a common operational unit ALU.
The major characteristic of ALSU is to perform all the logical, arithmetic, and shift operations. Operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are called arithmetic operations. Logical operation refers to operation on numbers and special character operations, and it connects two or more phrases of information(expressions). Shift micro-operations are operations for serial transfer of information.