Introduction
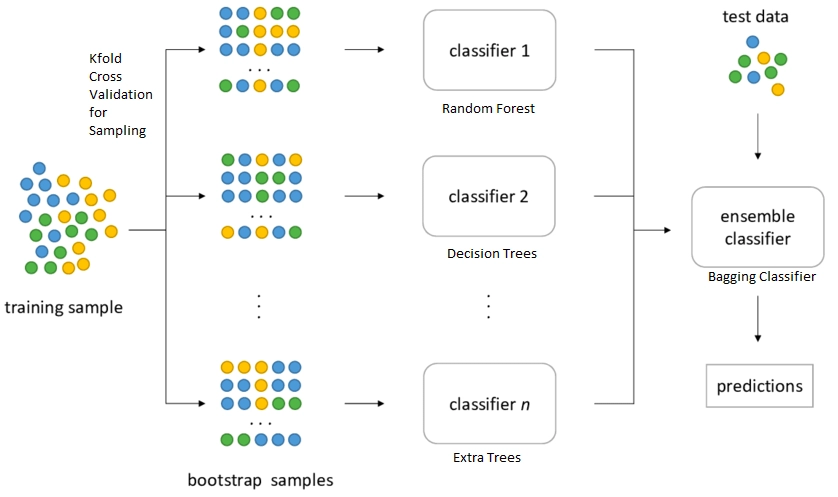
To understand bagging classification, we first need to understand the ensemble techniques. Ensemble means combining multiple models. This method trains various models with different datasets and gets the output. Ensemble techniques are of three types: bagging, boosting, and stacking; today, we will study bagging classification.
What is Bagging Classification?
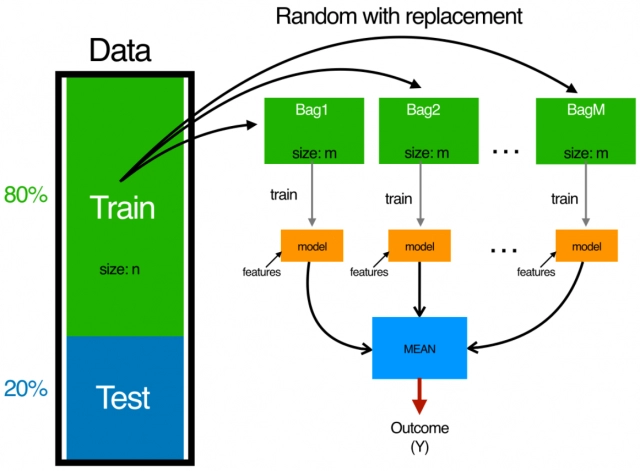
Initially, let us assume a particular problem statement has a dataset with n number of rows. Now will create multiple base models m and provide a sample of data for training the specific model. Note that the dataset provided to various models is always less than the original dataset, i.e., n. Also, the dataset provided is not the same for all the models; the original dataset is resampled to train the next model.
Source: Link
For example: Let us assume
Original dataset: 1,2,3,4,5,6
Then the dataset provided to various models will be row-wise resampled and hence will look like:
Resampled data 1: 6,3,2,5,1,4
Resampled data 2: 2,4,1,3,6,5
Resampled data 3: 4,1,3,6,5,2
Resampled data 4: 3,1,5,2,6,4
Resampled data 5: 5,2,1,3,6,4
The final result will be calculated based on voting or by calculating the mean of all the results of the respective models.
The bagging classification technique is also known as bootstrap aggregation.
Source: Link
Uses of Bagging Classification
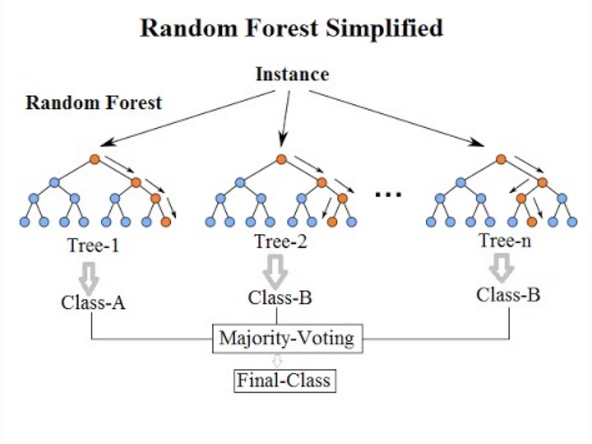
Bagging Classification is most commonly used in Random Forest models, be it classification or regression. In bagging classification, we have various base learners models; therefore, the base models are decision trees in a random forest. So to train the decision trees, feature sampling and row sampling with replacement are done. Once all the decision trees are trained on the replaced sampled data, they produce the required output or prediction based on a majority vote. Although, in regression, the final result is calculated by taking a mean of all the outcomes of the decision trees.
Source: Link
To know more about Random Forest, visit this article.