GroupLayout class
The declaration for javax.swing.GroupLayout class is listed below:
public class GroupLayout
extends Object
implements LayoutManager2
GroupLayout organizes its elements into groups and arranges them in a Container in a hierarchy. Group class instances are used to group things together.
SequentialGroup and ParallelGroup are two concrete classes that implement the abstract class along with Group.
While ParallelGroup aligns its children on top of one another, SequentialGroup arranges its children consecutively, one after another.
To build groups, the GroupLayout class has methods like createParallelGroup() and createSequentialGroup().
Each axis is handled separately by GroupLayout. In other words, there are two groups: one representing the horizontal axis and the other the vertical axis. In order to avoid an IllegalStateException from being thrown during layout or when the minimum, preferred, or maximum size is requested, each component must be present in both a horizontal and vertical group.
GroupLayout in Java Swing:
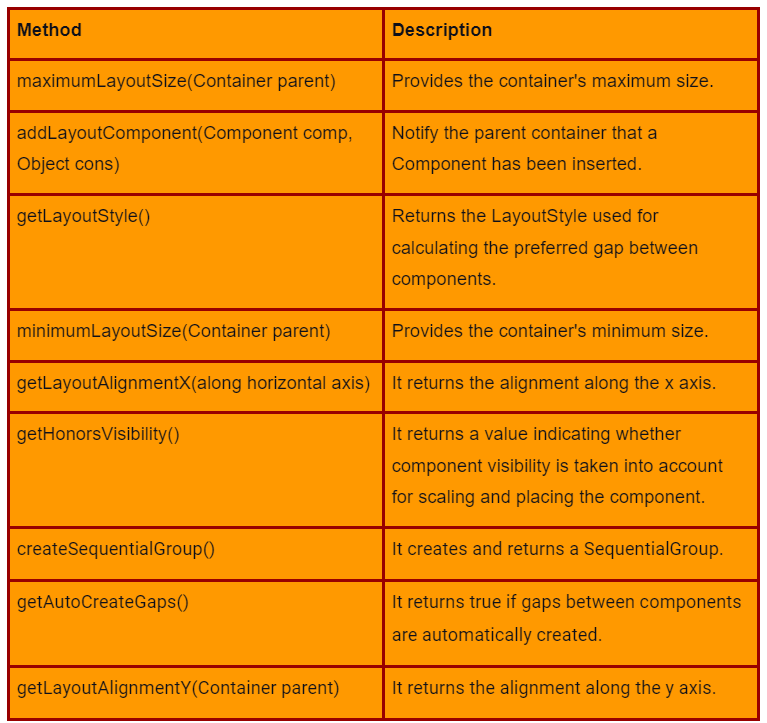
Common methods used in GroupLayout
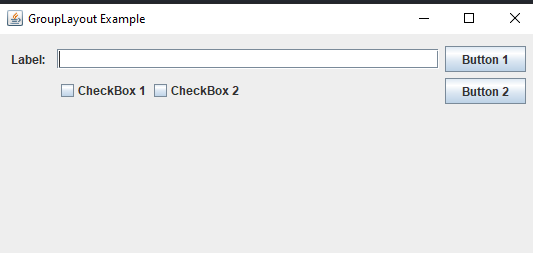
The components are arranged in a JFrame in the following example to demonstrate how GroupLayout is used. The JLabel, JTextField, JButton, and JCheckbox components are created. Then use the add() method to add them to the JFrame. The setLayout() method is used to set the layout.
import javax.swing.*;
//importing swing
import java.awt.Component;
import static javax.swing.GroupLayout.Alignment.*;
public class Main
{
// Initializing Main method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// defining frame
JFrame f = new JFrame("GroupLayout Example");
// using label
JLabel label = new JLabel("Label:");
// using textField
JTextField textField = new JTextField();
// defining button 1
JButton btn1 = new JButton("Button 1");
// defininh button 2
JButton btn2 = new JButton("Button 2");
// defining checkBox 1
JCheckBox checkBox1 = new JCheckBox("CheckBox 1");
// deining checkBox 2
JCheckBox checkBox2 = new JCheckBox("CheckBox 2");
// using GroupLayout
GroupLayout layout = new GroupLayout(f.getContentPane());
// setting the layout of components in the frame
f.getContentPane().setLayout(layout);
// creating empty spaces
layout.setAutoCreateGaps(true);
// creating an empty space container
layout.setAutoCreateContainerGaps(true);
// defining the horizontal group
layout.setHorizontalGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
// Adding label
.addComponent(label)
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(LEADING)
// Adding text field
.addComponent(textField)
// Adding sequential group
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(LEADING)
// Adding the 1st checkbox
.addComponent(checkBox1))
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(LEADING)
// Adding the 2nd checkbox
.addComponent(checkBox2))))
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(LEADING)
// Adding button 1
.addComponent(btn1)
// Adding button 2
.addComponent(btn2)));
//linking the size of components regardless of their location
layout.linkSize(SwingConstants.HORIZONTAL, btn1, btn2);
//Creating the vertical group
layout.setVerticalGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(BASELINE)
// Adding label
.addComponent(label)
// Adding text field
.addComponent(textField)
// Adding button 1
.addComponent(btn1))
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(LEADING)
// Adding sequential group
.addGroup(layout.createSequentialGroup()
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(BASELINE)
// Adding the 1st checkbox
.addComponent(checkBox1)
// Adding the 2nd checkbox
.addComponent(checkBox2))
// Adding parallel group
.addGroup(layout.createParallelGroup(BASELINE)))
// Adding button 2
.addComponent(btn2)
)
);
f.pack();
f.show();
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using a Java layout manager within an application?
It is simpler to change and revise placements, widths, fonts, and the general look and feel of the container, a layout manager is favored. Layout managers also guarantee reuse, allowing for the usage of an existing component's structure and definition in other containers within the same or separate programs.
How many layout managers are available in Java?
The Java.awt package provides five layout managers: FlowLayout, BorderLayout, GridLayout, CardLayout, and GridBagLayout.
What are the advantages of a good layout?
The entire organization gains from a well-designed layout in addition to individuals involved in the manufacturing process. It leads to increased productivity, a shorter manufacturing cycle, lower costs, more inventory turnover, and ultimately higher customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
In this article, we have extensively discussed group layout in Java, the types of group layout methods, swing class in Java, and examples of group layout. We started with a brief introduction to group layout in java and swing class, then we saw the declaration of group layout, and different methods used in GroupLayout, and in the end we understood GroupLayout with the help of a coded example.
After reading about Grouplayout in Java, are you not feeling excited to read/explore more articles on the topic of Swing and Java? Don't worry; Coding Ninjas has you covered. If you want to learn more about Java, then you can refer to links, basics of Java, Why is Java Platform Independent, JDK, Java.util, and Java platform.
Refer to our Guided Path on Coding Ninjas Studio to upskill yourself in Data Structures and Algorithms, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, and many more! If you want to test your competency in coding, you may check out the mock test series and participate in the contests hosted on Coding Ninjas Studio! But suppose you have just started your learning process and are looking for questions asked by tech giants like Amazon, Microsoft, Uber, etc. In that case, you must look at the problems, interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations.
Nevertheless, you may consider our paid courses to give your career an edge over others!
Do upvote our blogs if you find them helpful and engaging!
Happy Learning!







