Introduction
JavaFX is a collection of media and graphics packages that provide developers the ability to create, design, test, debug, and deploy rich client applications that work consistently on various platforms.
In this blog, we will discuss the JavaFX Box class present in the JavaFX framework. We will look into the different types of constructors and methods present inside the Box class. We will also discuss how we can use these different methods inside our code.

Source: Wikipedia
Box Class
The Box class is a part of JavaFX. The Box class is used in the JavaFX application to draw a box. We can create 3D shapes with rectangular faces using the box. The box is centered at the origin. The following graphic shows a cube's (box) height, width, and depth.
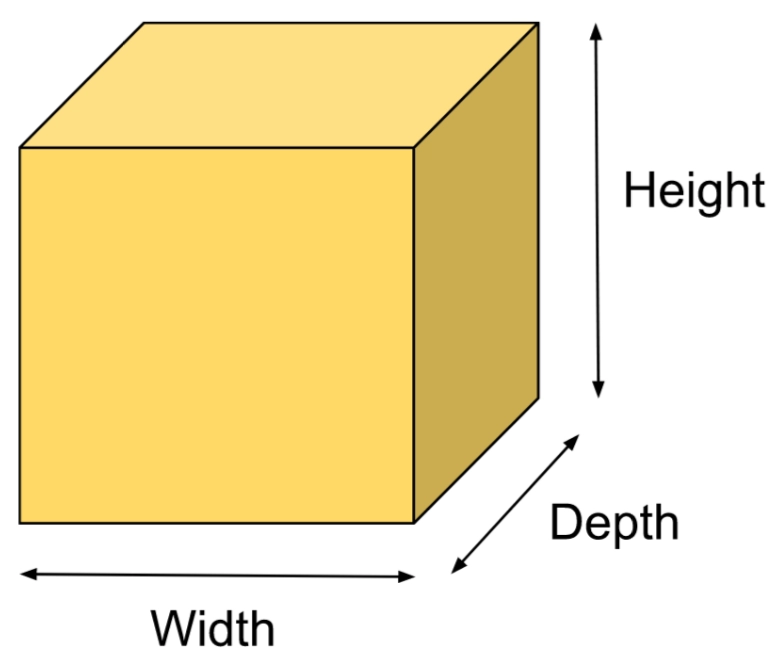
The box is a part of the JavaFX framework and the javafx.scene.shape.Box class contains all the methods required for our goal.
Constructors
There are two different types of constructors available in theJavaFX box:
-
public Box(): Creates an empty Box class instance. It requires setters to set values of height, width, and depth.
- public Box(double width_value, double height_value, double depth_value): It is the parameterized constructor and allows us to pass width, height, and depth values in its constructor.
Common Methods
The class contains various commonly used methods that are described below.
-
setDepth(double val): It is used to set the depth of the box. It represents the Z-dimension.
-
setHeight(double val): It is used to set the height of the box. It represents the Y-dimension.
- setWidth(double val): It is used to set the height of the box. It represents the X-dimension.
Usage
We got some ideas about JavaFX Box class and the different functions and constructors available in it. But where do we actually use the Box class in our JavaFX application? Whenever we want to draw boxes in our application we use JavaFX Box class. The Box class is used as the layout in JavaFX applications. Now, let’s see the implementation.





