Introduction
Associative memory can be a memory unit whose database can be identified as accessible by the data itself instead of an address or memory location. This way, it optimizes the process of searching the data. It is also termed as an associative array or associative storage. But, one popular term used for associative memory is content addressable memory (CAM). In this blog, we will learn about the concept of associative memory along with its hardware organization and operations of read-write. Let's begin!!
Recommended Topic, Microinstruction in Computer Architecture
What is Associative Memory
Associative memory is a memory unit whose database can be accessed by the data or content instead of an address or memory location. It is also called content addressable memory or CAM. It helps optimize searching any data as the searching process does not involve addressing, but it works on data.
Hardware Organization
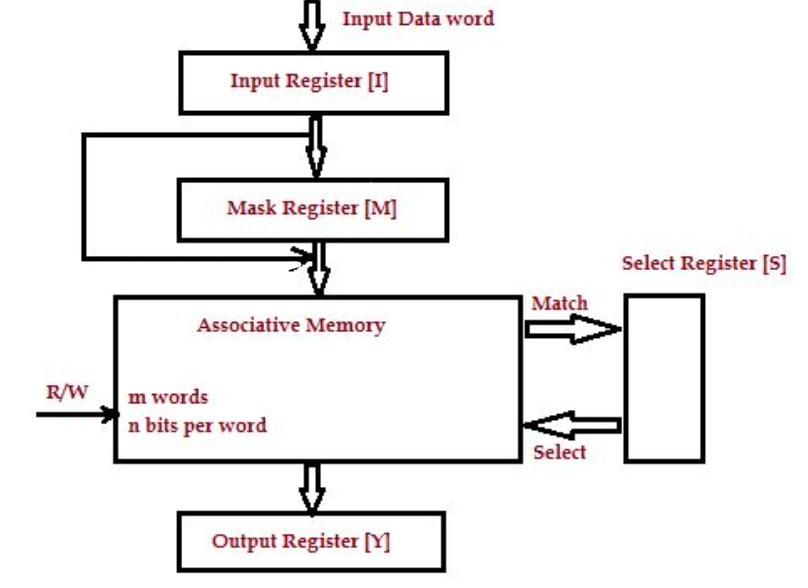
Block diagram of Associative memory
Source: https://tutorialsinhand.com/
The diagram shown above is a block diagram of the hardware organization of associative memory. It includes input register, mask register, select register and output register, and an associative array with m words, each with n bits.
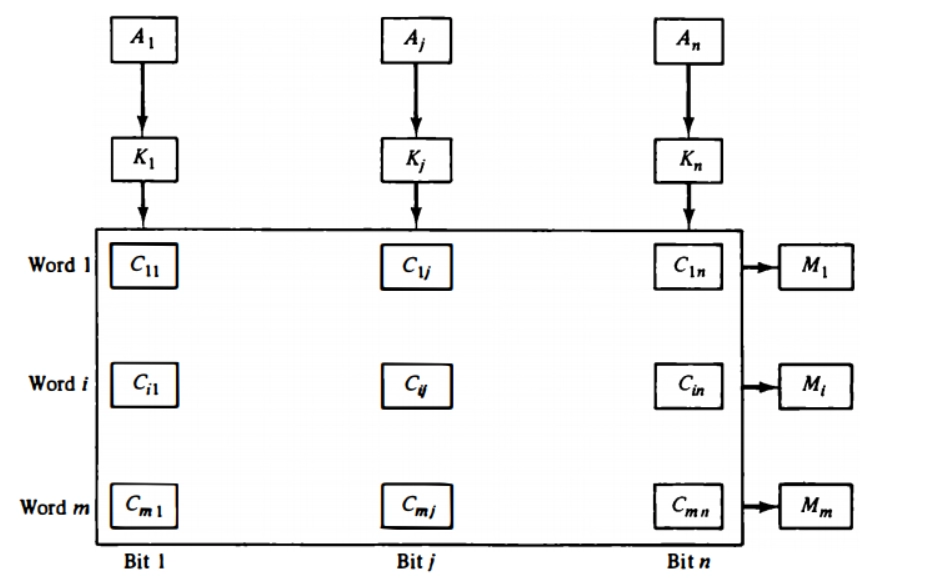
Here, the function of the input register is to hold the content that we want to write or search in the associative memory. At the moment, it can hold only one word having length let us say n. The function of the mask register is to provide a mask for selecting a specific key or field in the word of the input register. The input register can hold single word length data, where length is n so that the maximum value of the mask register's length can be n. The function of the select register is to contain m-bits, one for each memory's word. If the input data of the input register get compared with the key in the m registers, and we get a match, then that particular bit is set in the select register. The function of the output register is to contain the data word that got matched retrieved from the associative memory.
You can also read about - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics