Introduction
In computer Organisation and Architecture (COA), we study a computer system's internal working and structure and how the various components are organized for their efficient use.
Pipelining is one of COA techniques used for decomposing a task into smaller subtasks in a pipeline manner for improving the system's performance. In this way, subtasks are arranged in sequential order in a pipeline, where the output of one subtask is used as input for the next subtask. The main advantage of pipelining is the simultaneous execution of various subtasks, which improves the system's throughput.
Also Read - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics
Let's understand the advantage of a pipeline through a simple example:
Suppose the task is to take two integers as input and print their sum as output.
The system will first take the two integers as input, compute their sum, and then print it. Here, another set of two integers will wait until the sum of the previous set of integers is printed. Also, when the system is computing the sum, the parts of the system taking input or printing output are left unused. In this way, the resources are not utilized efficiently.
But if will use a pipeline, we can divide this task into the following subtasks:
- Take input
- Compute sum
- Print the sum
And, if these three subtasks are executed parallelly, we will get faster execution of the task. While the system is computing the sum of two integers, it will parallelly take the next set of integers as input, and this way, the number of tasks in a given interval of time will increase.
There are mainly two types of pipelines in COA. They are:
- Arithmetic Pipeline
- Instruction Pipeline
This article will discuss the 'Instruction Pipeline' in detail.
Recommended Topic, Microinstruction in Computer Architecture
Instruction Pipeline
Instruction pipelines are used to divide the task of executing a stream of instructions into subtasks to be executed in different pipeline segments to improve the throughput of the computer system. For example, if we have a stream of instructions, then one segment of the pipeline can read the instructions while another segment can decode the previous instruction. In this way, more than one instruction will be handled simultaneously by the computer system that will improve its throughput. The instruction pipeline will be more efficient if the instructions are divided into equal duration segments.
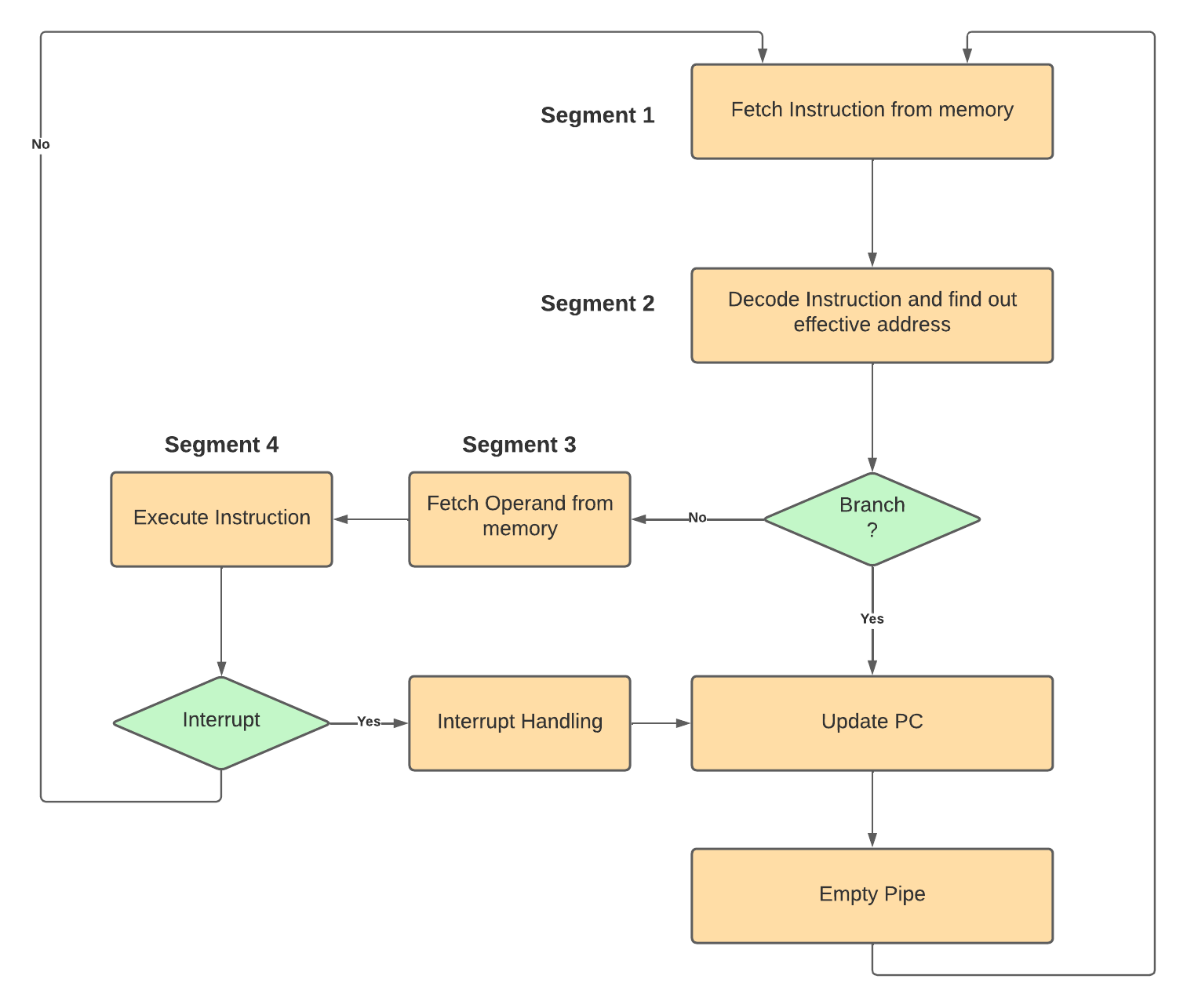
A typical example of instruction pipeline used by computer systems consists of the following segments:
- Segment 1: This segment will fetch the instruction from the memory
- Segment 2: This segment will decode the instruction and find out the effective address
- Segment 3: This segment will fetch the operands from the memory
- Segment 4: This segment will execute the instruction
The diagram below shows the instruction pipeline which we have discussed here: