Time-shared common bus
In any multiprocessor system, the time-shared common bus interconnection structures provide a common communication path by connecting all the functional units like I/O processor, processor, memory unit, etc. The figure below displays a multiprocessor system with a common communication path (single bus).

A single bus multiprocessor system
The processor needs the common bus to communicate with a functional unit to transfer data. To do so, the processor first checks if the bus is available or not. The processor can only use the common bus if it is free. The processor puts the destination unit address on the common bus, and the destination unit identifies it. A command is issued to tell the receiver unit what work is to be done to communicate with a functional unit. The other functional units at that time will be either busy in internal operations or will sit free, waiting to get the common bus.
We can resolve memory access conflict with methods such as First-In-Out (FIFO) queues, static & fixed priorities, and daisy chains can be used.
Multiport memory
A multiport memory structure employs separate buses for every memory module and CPU. Every processor in a multiport memory is connected to each memory unit. The below figure shows multiport memory interconnection structures.
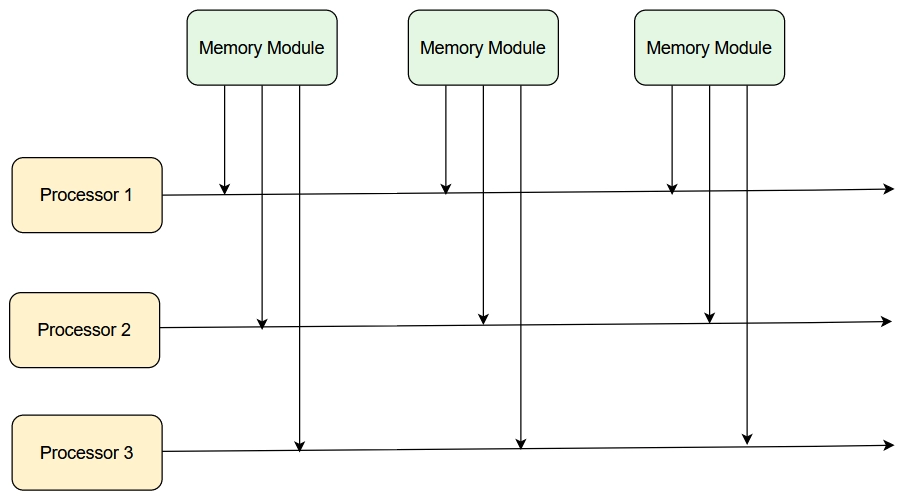
Multiport memory system with three processor
A processor bus consists of the data, control lines, and address required for communication with the memory. The memory unit is said to have three ports, and each port connects with one of the buses. The module should have internal control logic to determine which port will have access to memory at the given time.
We can resolve Memory access conflicts by assigning fixed priorities to every memory port.
Must Read - Memory hierarchy in computer network Demultiplexer
Crossbar switch
The crossbar switch system consists of several intersection crosspoints between processor buses and memory module paths. Let's understand its structure with the below figure.

Crossbar switch organization
In every crosspoint, the tiny box represents a switch that can obtain the path from a processor to the memory module. Every switch point has to control logic for setting up the transfer path among a processor and memory unit. It can calculate the address placed in the bus to obtain if its specific module is addressed. In addition, it can eliminate multiple requests to access the same memory module on a priority basis.
The functional design of the crossbar switch is as follows:
The circuit contains multiplexers that choose the address, data, and control from the CPU for communication with any memory unit. Arbitration logic establishes priority levels to select only one CPU when two or more CPUs attempt to access the same memory. The multiplexer can be handled by the binary code produced by the priority encoder within the arbitration logic.
A crossbar switch system allows simultaneous transfers from all memory units because separate paths are associated with all the memory modules.
Also read, microprogrammed control unit
Multistage switching network
The multistage network system uses a 2×2 crossbar switch. It has two inputs (A and B) and two outputs (0 and 1). To establish the connection between the input terminal and output terminals, control inputs CA & CB are associated.

Multistage switching network
Hypercube system
Hypercube system is a binary n-cube architecture. In the Hypercube system, we can connect 2*n processors, and each of the processors forms a node for the cube. A node can be an I/O interface, memory module, and processor. A processor at any node has a communication path that directly goes to n other nodes (i.e., a total of 2n nodes). There are a total of 2n distinct n-bit binary addresses.
Also know about Input-Output Processor in detail.
Must Read hardwired and microprogrammed control unit
FAQs
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the time-shared common bus?
The advantage of using the time-shared common bus is that it is easy to implement and inexpensive. The disadvantage is that only one bus is available for data transfer between multiple logical units, allowing only one processor to work at a time.
-
What are the factors affecting the performance of buses?
Among all the Interconnection structures, factors affecting the performance of the buses are:
* Data Width.
* Numbers of active devices on the bus.
* Error Detection method.
* Synchronization of data transfer.
-
Why isn't the common bus system used even when it is much easy &simple?
Although Time-shared common bus system is much easy and simple to implement, we don't use it much because of the following reasons:
* It uses only one bus, so if any malfunction occurs, our complete system will fail.
* At a time, only one processor unit can communicate with any other functional unit.
-
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a Multiport memory system?
The multiport memory system has the advantage of a high transfer rate because of multiple paths between functional units. The only disadvantage of this system is that it is very expensive as it uses multiple cables and connectors.
Key Takeaways
In this article, we have extensively discussed Interconnection structures in a computer system like Time-shared common bus, Multiport memory, Crossbar switch, Multistage switching network, and Hypercube system.
You can also consider our Online Coding Courses such as the DSA in Python, C++ DSA Course, DSA in Java Course to give your career an edge over others.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding reversing an array in Java and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on Pipelining and Modes of Transfer. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow. Happy Coding!









