Introduction
Before diving into the problem, let’s first understand the width or breadth of a binary tree. The number of nodes present at the given level can determine the width of a binary tree. To be more specific, the maximum number of nodes at any binary tree level is the maximum width of a binary tree.

The maximum width of a binary tree is the count of nodes without children. It represents the minimum nodes that must be traversed before needing to decide on the next node to visit.
Let’s understand it with some examples:
Example - 1:
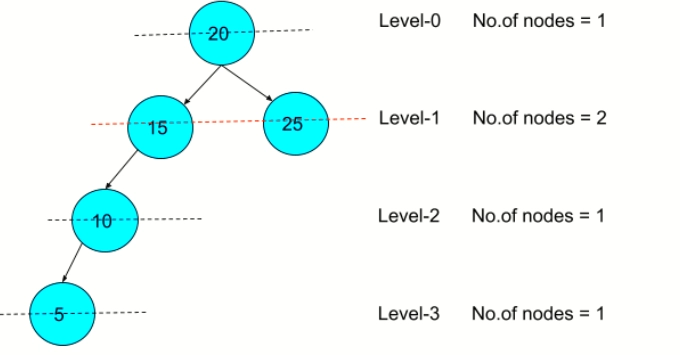
Since the maximum number of nodes present at Level-1 is 2, the maximum width of the binary tree is 2
Example-2:

As you can see, the maximum number of nodes present at level 2 is 4; hence the maximum width of the binary tree is 4.
Now that you know how to find the maximum width of a binary tree, we need to build an algorithm that will allow us to return the maximum width for any binary tree.
It is recommended to Implement the stated maximum width in binary tree problem on your own before moving to the solution.
You can obtain a greater understanding of data structures and algorithms by solving on your own the stated maximum width problem in a binary tree. By addressing the problem on your own, you'll have the chance to experiment with different strategies, spot potential challenges, and improve your problem-solving abilities.
Let's discuss the approach to solve the stated problem:
Maximum Width using Level-order Traversal
The naive yet effective approach can be using Level-wise traversal. As we aim to find the maximum number of nodes level-wise thus, employing Level order Traversal (or Breadth-first search) will suffice.
Level-order traversal or breadth-first search starts traversing at the tree from root and explores all nodes at the present level before moving on to the nodes at the next depth level.
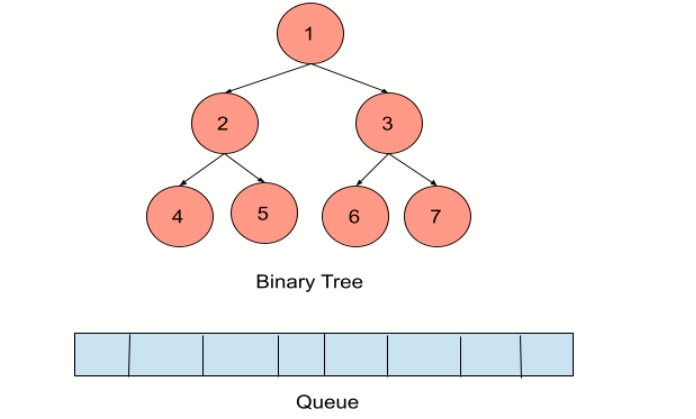
Consider the below diagram:
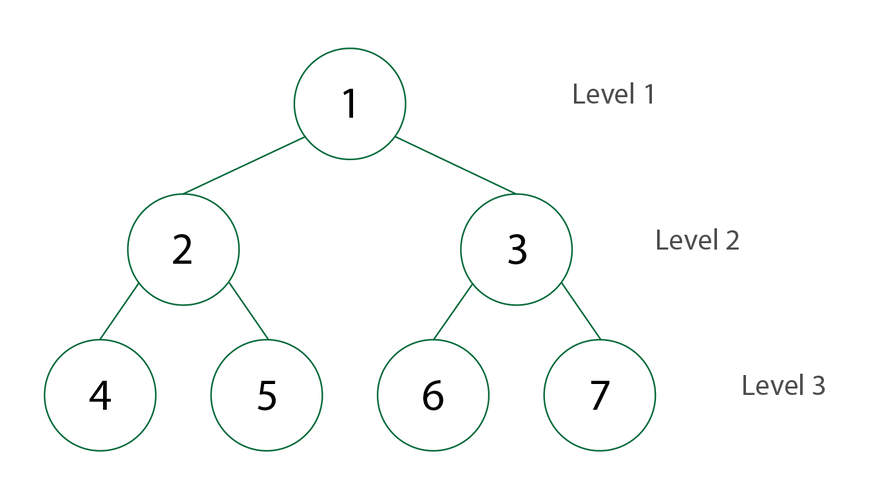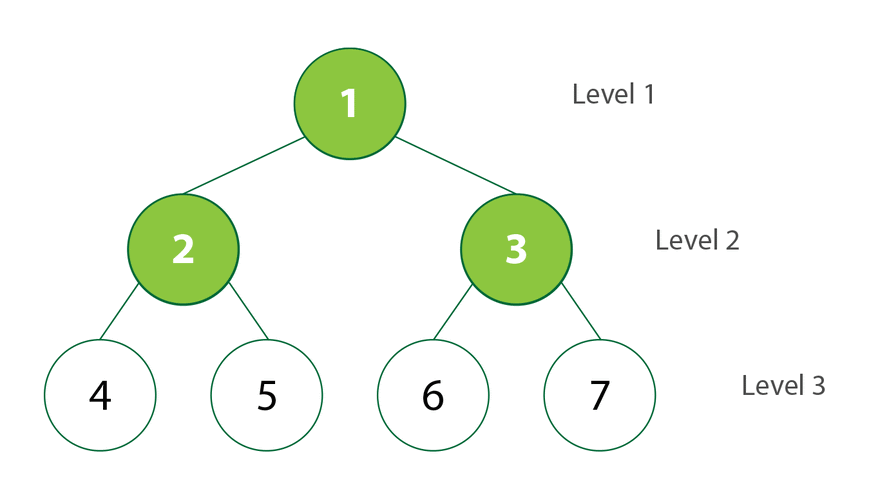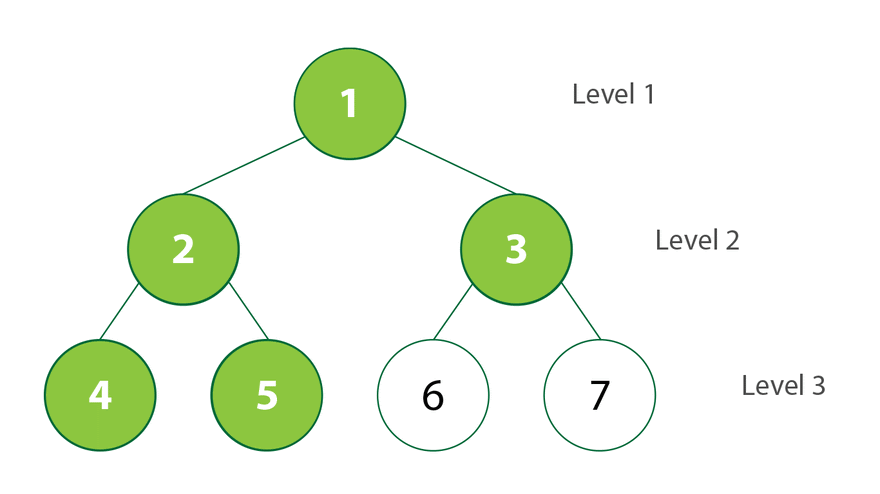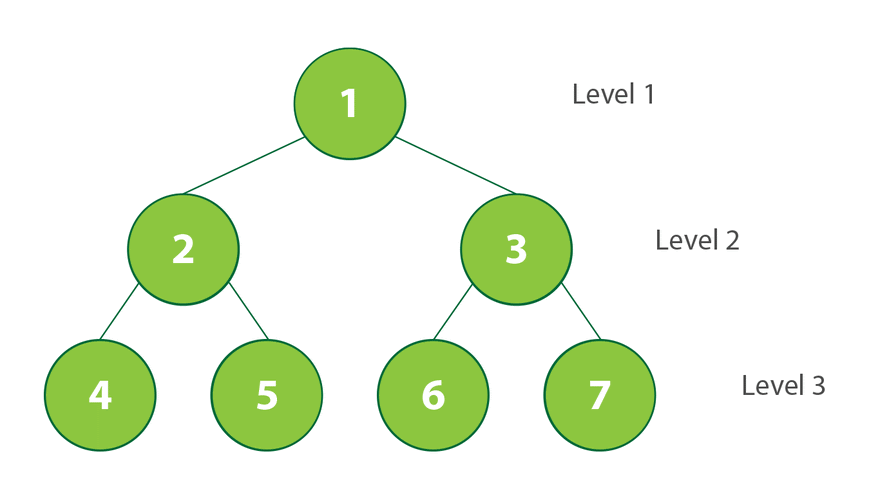
This is how the Level order traversal works in trees or any data structure.
Now let’s understand the algorithm for finding the maximum width of a binary tree using the Level-order traversal.

In the given binary tree:
Level 1 has 1 node, so maxWidth = 1
Level 2 has 2 node, so maxWidth = 2( 2 > 1)
Level 3 has 4 node, so maxWidth = 4( 4 > 2)
Hence, the maximum width will be 4.
Level Order Traversal without queue
Without using a queue, level order traversal in a binary tree involves tracking each level's nodes separately, usually through depth-first or recursion-based approaches. This method typically requires additional bookkeeping and may not be as efficient as using a queue. In this method:
- You would typically use a recursive approach.
- Start by calculating the height of the binary tree. Then, iterate from height 1 to the maximum height.
- At each level, traverse the tree and print the nodes encountered at that level.
- You might need a helper function that takes the root node and the current level as parameters.
- This method involves multiple passes through the tree and might not be as efficient as using a queue.
Level Order Traversal using Queue
Level order traversal using a queue involves iterating through each level of a binary tree horizontally. Starting from the root node, each level's nodes are processed sequentially by enqueueing child nodes and dequeueing parent nodes. This method ensures nodes are visited in a breadth-first manner, making it efficient and easy to implement. In this method:
- Initialize a queue and enqueue the root node.
- Begin a loop that continues until the queue is empty.
- Inside the loop, dequeue a node, process it (print its value, for example), and enqueue its children (if any) from left to right.
- Repeat this process until all nodes are processed.
- This method ensures that nodes are visited level by level, from left to right, which is the characteristic of level order traversal.
- Using a queue helps in keeping track of the nodes to be processed at each level efficiently, ensuring a breadth-first search pattern.
Also read - Boundary Traversal of Binary Tree
Algorithm
-
Define the Node class, which contains three attributes: data, left, and right where, the left child of the node is represented by left, and the right child of the node is represented by right
-
When a node is constructed, data is passed to the node's data attribute, and both left and right are set to null
-
Create a new class with the root attribute. The root represents the tree's root node and sets its value to null
- findMaxWidth() will find out the maximum width of a binary tree
-
The variable maxWidth will keep track of the total number of nodes in each level
-
The queue is used to traverse the binary tree on a level-by-level basis
-
The function also determines if the root is null, indicating that the tree is empty
-
If this is not the case, add the root node to the queue. Variable level_nodes keep track of the number of nodes in each level
- Remove the node from the front of the queue and add its left and right children to the queue if the number of level_nodes > 0

-
In the above diagram, node 1 will be eliminated in the first iteration, and its children nodes 2 and 3 will be added to the queue. Node 2 will be eliminated in the second iteration, and its offspring 4 and 5 will be added to the queue, and so on
-
MaxWidth is a variable that stores the maximum width (maxWidth, level_nodes). As a result, it will always represent the maximum number of nodes at any given time
5. Finally, Print the maxWidth
Now, let’s look at the Implementation:
Implementation in Java
Output
Maximum width of a binary tree: 4
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes present in a binary tree. Since each node is processed once, therefore the time complexity is O(N).
Space Complexity: The Space Complexity is O(W), where W is the maximum width of a binary tree. Because, In level order traversal, a queue is kept whose maximum size at any given time can be as large as the binary tree's maximum width. In the worst case, it can be O(N), where N is the number of nodes present in a binary tree.
Implementation in python
Output
Maximum width of a binary tree: 4
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes present in a binary tree. Since each node is processed once, therefore the time taken will be O(N).
Space Complexity: O(W), where W is the maximum width of a binary tree. Because, In level order traversal, a queue is kept whose maximum size at any given time can be as large as the binary tree's maximum width. In the worst case, it can be O(N), where N is the number of nodes present in a binary tree.
Pictorial Representation of the above example in implementation:-