An array processor is a computer/processor with a specific architecture for dealing with numerical arrays (e.g., matrices). An array processor can be created as a self-contained unit connected to a central computer by an I/O port or internal bus. It can be built as a distributed array processor, with processing units distributed across and closely linked to a section of the computer's memory.
Recommended Topic, Microinstruction in Computer Architecture
Classification of Array Processors in Computer Architecture
Array processors can be divided into two categories:
- Attached Array Processors
- SIMD(Single Instruction Stream, Multiple Data Stream) Array Processors
We will go through the explained detail in the sections below.
Also Read - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics
1. Attached Array Processor
The attached array processor is the auxiliary processor connected to a general-purpose computer to enhance and improve the machine's performance in numerical computational tasks. It provides excellent performance by using numerous functional units in parallel processing.
The attached array processor includes a common processor with an input/output interface and a local memory interface.
The main memory and the local memory are linked.
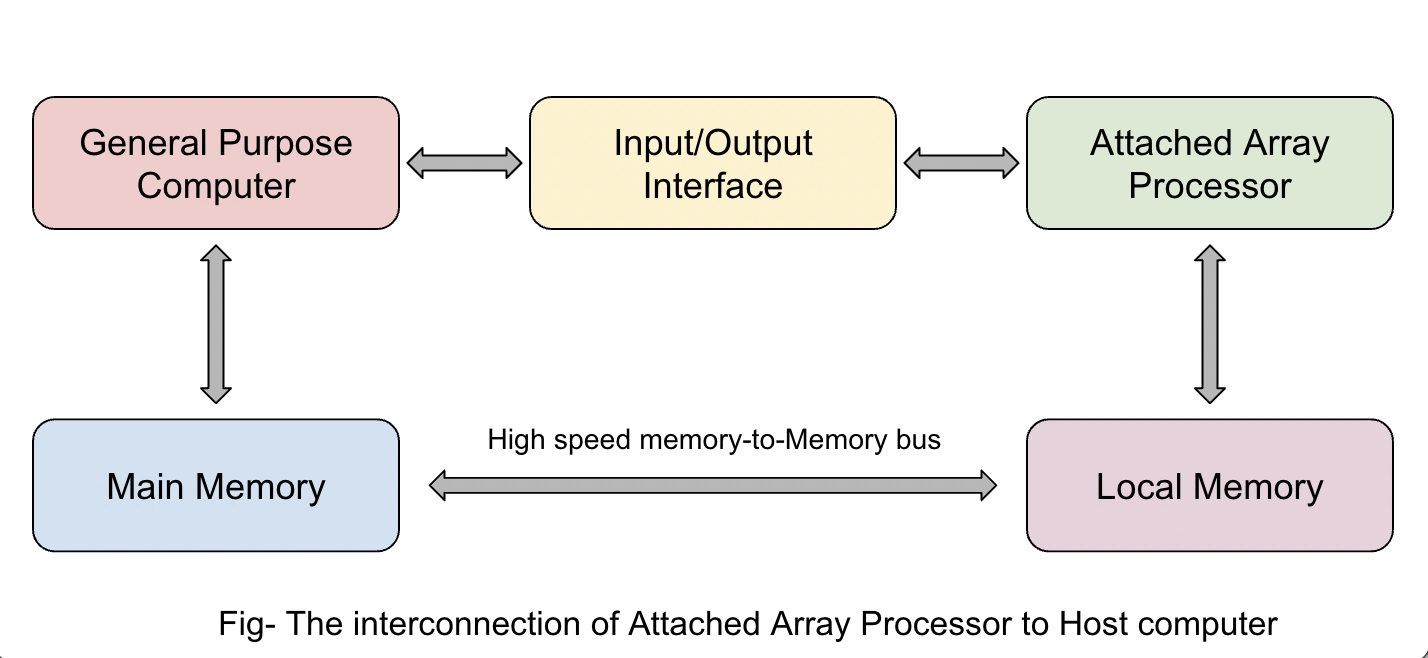
The attached array processor intends to improve the performance of the host computer in specific numeric computations.
2. SIMD Array Processor
SIMD refers to the organization of a single computer with multiple parallel processors. The processing units are designed to work together under the supervision of a single control unit, resulting in a single instruction stream and multiple data streams.
An array processor's general block diagram is given below. It comprises several identical processing elements (PEs), each with its local memory M. An ALU and registers are included in each processor element. The master control unit controls the processing elements' actions. It also decodes instructions and determines how they should be carried out.
The program is stored in the main memory. The control unit retrieves the instructions. Vector instructions are sent to all PEs simultaneously, and the results are stored in memory.

The ILLIAC IV computer, manufactured by the Burroughs Corporation, is the most well-known SIMD array processor. Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) processors are highly specialized computers. They're only good for numerical issues that can be stated as vectors or matrices; they're not suitable for other kinds of computations.
Configurations of SIMD
1. Array processors that use RAM(Random Access Memory) are also known as Dedicated Memory Organisations.
- ILLIAC-IV
- CM-2
- MP-1
2. An associative processor that uses content-accessible memory is known as Global Memory Organisation.
- BSP
Usage of Array Processors
- Array processors enhance the total speed of instruction processing.
- Most array processors' design optimizes its performance for repetitive arithmetic operations, making it faster at vector arithmetic than the host CPU. Since most Array processors run asynchronously from the host CPU, the system's overall capacity is thus improved.
- Array Processors have their own local memory, providing additional extra memory to systems with limited memory. This is an essential consideration for the systems with a limited physical memory or address space.




